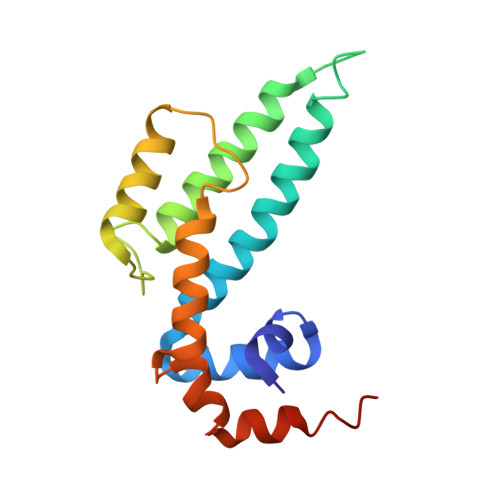
Structural Studies Reveal Unique Non-canonical Regulators of G Protein Signaling Homology (RH) Domains in Sorting Nexins.
Zhang, Y., Chen, R., Dong, Y., Zhu, J., Su, K., Liu, J., Xu, J.(2022) J Mol Biology 434: 167823-167823
- PubMed: 36103920
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167823
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WF6, 7WF8, 7WF9 - PubMed Abstract:
As a subgroup of sorting nexins (SNXs) that contain regulator of G protein signaling homology (RH) domain, SNX-RH proteins, including SNX13, SNX14 and SNX25, were proposed to play bifunctional roles in protein sorting and GPCR signaling regulation. However, mechanistic details of SNX-RH proteins functioning via RH domain remain to be illustrated. Here, we delineate crystal structures of the RH domains of SNX13 and SNX25, revealing a homodimer of SNX13 RH domain mediated by unique extended α4 and α5 helices, and a thiol modulated homodimer of SNX25-RH triggered by a unique cysteine on α6 helix. Further studies showed that RH domains of SNX-RH do not possess binding capacity toward Gα subunits, owing to the lack of critical residues for interaction. Thus, this study identifies a group of novel non-canonical RH domains that can act as a dimerization module in sorting nexins, which provides structural basis for mechanism studies on SNX-RH protein functions.
- State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510530, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
Organizational Affiliation: