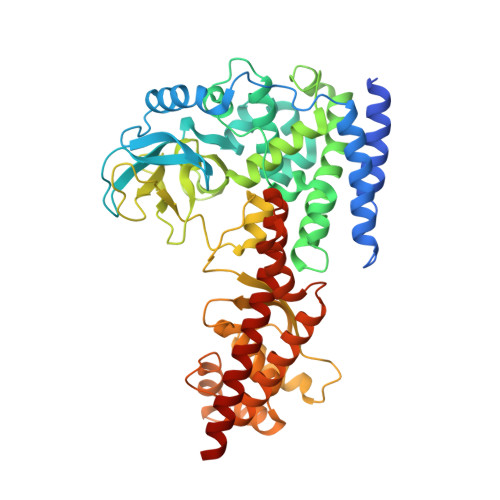
Histidine methyltransferase SETD3 methylates structurally diverse histidine mimics in actin.
Hintzen, J.C.J., Ma, H., Deng, H., Witecka, A., Andersen, S.B., Drozak, J., Guo, H., Qian, P., Li, H., Mecinovic, J.(2022) Protein Sci 31: e4305-e4305
- PubMed: 35481649
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4305
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W28, 7W29 - PubMed Abstract:
Actin histidine N τ -methylation by histidine methyltransferase SETD3 plays an important role in human biology and diseases. Here, we report integrated synthetic, biocatalytic, biostructural, and computational analyses on human SETD3-catalyzed methylation of actin peptides possessing histidine and its structurally and chemically diverse mimics. Our enzyme assays supported by biostructural analyses demonstrate that SETD3 has a broader substrate scope beyond histidine, including N-nucleophiles on the aromatic and aliphatic side chains. Quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical molecular dynamics and free-energy simulations provide insight into binding geometries and the free energy barrier for the enzymatic methyl transfer to histidine mimics, further supporting experimental data that histidine is the superior SETD3 substrate over its analogs. This work demonstrates that human SETD3 has a potential to catalyze efficient methylation of several histidine mimics, overall providing mechanistic, biocatalytic, and functional insight into actin histidine methylation by SETD3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physics, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.