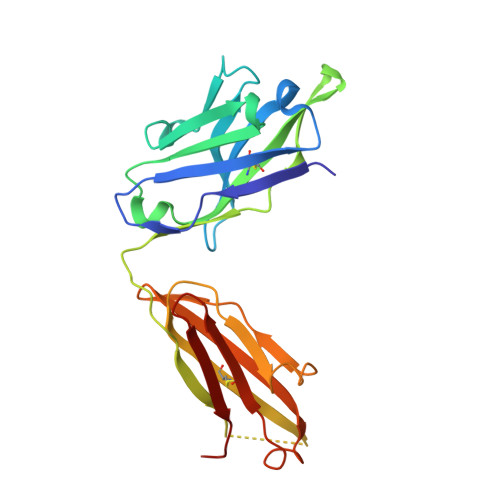
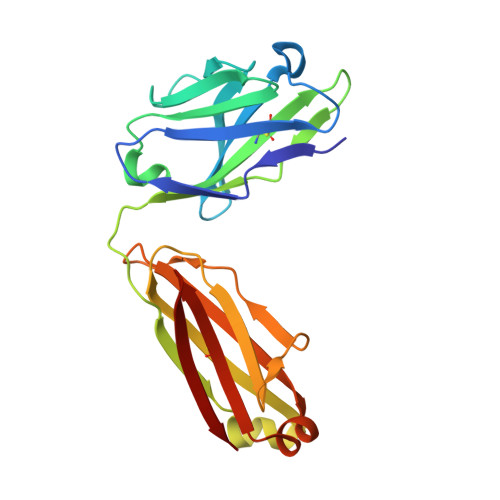
Structures of drug-specific monoclonal antibodies bound to opioids and nicotine reveal a common mode of binding.
Rodarte, J.V., Baehr, C., Hicks, D., Liban, T.L., Weidle, C., Rupert, P.B., Jahan, R., Wall, A., McGuire, A.T., Strong, R.K., Runyon, S., Pravetoni, M., Pancera, M.(2023) Structure 31: 20-32.e5
- PubMed: 36513069
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2022.11.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7U61, 7U62, 7U63, 7U64 - PubMed Abstract:
Opioid-related fatal overdoses have reached epidemic proportions. Because existing treatments for opioid use disorders offer limited long-term protection, accelerating the development of newer approaches is critical. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are an emerging treatment strategy that targets and sequesters selected opioids in the bloodstream, reducing drug distribution across the blood-brain barrier, thus preventing or reversing opioid toxicity. We previously identified a series of murine mAbs with high affinity and selectivity for oxycodone, morphine, fentanyl, and nicotine. To determine their binding mechanism, we used X-ray crystallography to solve the structures of mAbs bound to their respective targets, to 2.2 Å resolution or higher. Structural analysis showed a critical convergent hydrogen bonding mode that is dependent on a glutamic acid residue in the mAbs' heavy chain and a tertiary amine of the ligand. Characterizing drug-mAb complexes represents a significant step toward rational antibody engineering and future manufacturing activities to support clinical evaluation.
- Vaccine and Infectious Disease Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, WA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: