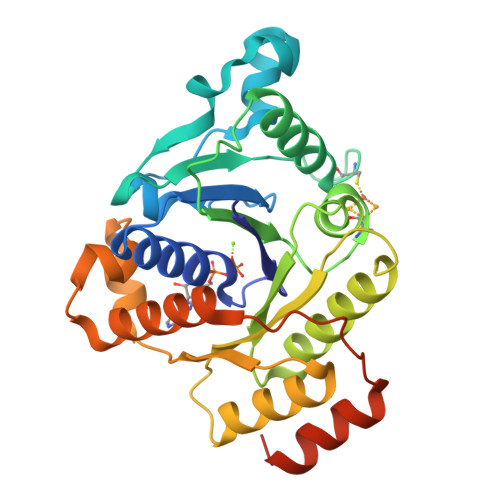
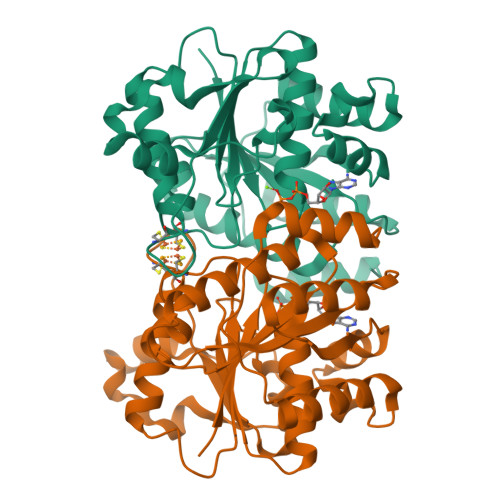
Selenocyanate derived Se-incorporation into the Nitrogenase Fe protein cluster.
Buscagan, T.M., Kaiser, J.T., Rees, D.C.(2022) Elife 11
- PubMed: 35904245
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.79311
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7T4H, 7TNE, 7TPN, 7TPO, 7TPV, 7TPW, 7TPX, 7TPY, 7TPZ, 7TQ0, 7TQ9, 7TQC, 7TQE, 7TQF, 7TQH, 7TQI, 7TQJ, 7TQK - PubMed Abstract:
The nitrogenase Fe protein mediates ATP-dependent electron transfer to the nitrogenase MoFe protein during nitrogen fixation, in addition to catalyzing MoFe protein-independent substrate (CO 2 ) reduction and facilitating MoFe protein metallocluster biosynthesis. The precise role(s) of the Fe protein Fe 4 S 4 cluster in some of these processes remains ill-defined. Herein, we report crystallographic data demonstrating ATP-dependent chalcogenide exchange at the Fe 4 S 4 cluster of the nitrogenase Fe protein when potassium selenocyanate is used as the selenium source, an unexpected result as the Fe protein cluster is not traditionally perceived as a site of substrate binding within nitrogenase. The observed chalcogenide exchange illustrates that this Fe 4 S 4 cluster is capable of core substitution reactions under certain conditions, adding to the Fe protein's repertoire of unique properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, United States.