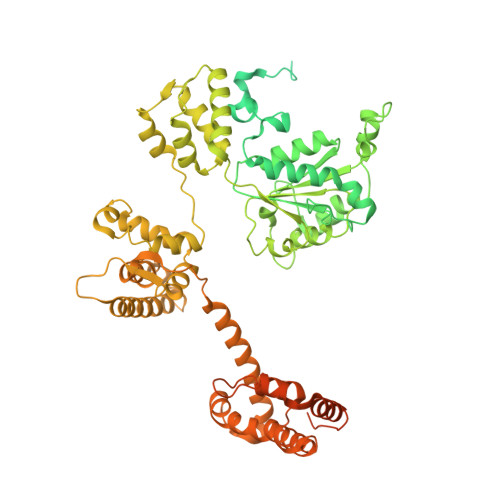
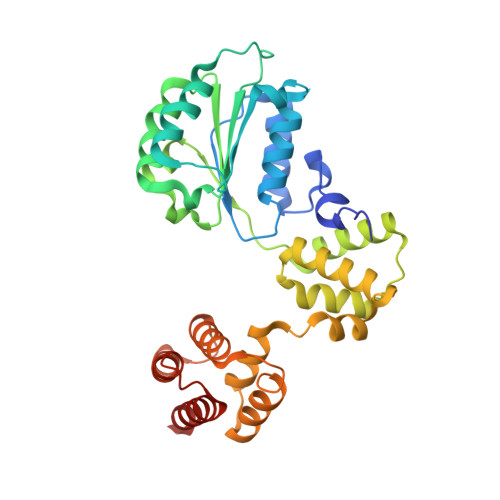
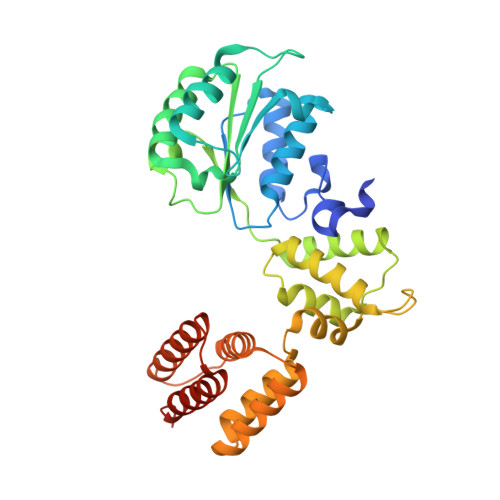
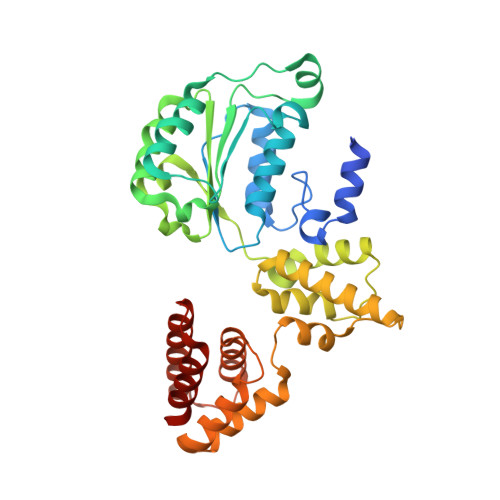
Cryo-EM structures reveal high-resolution mechanism of a DNA polymerase sliding clamp loader.
Gaubitz, C., Liu, X., Pajak, J., Stone, N.P., Hayes, J.A., Demo, G., Kelch PhD, B.A.(2022) Elife 11
- PubMed: 35179493
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.74175
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7THJ, 7THV, 7TI8, 7TIB, 7TIC, 7TID, 7TKU - PubMed Abstract:
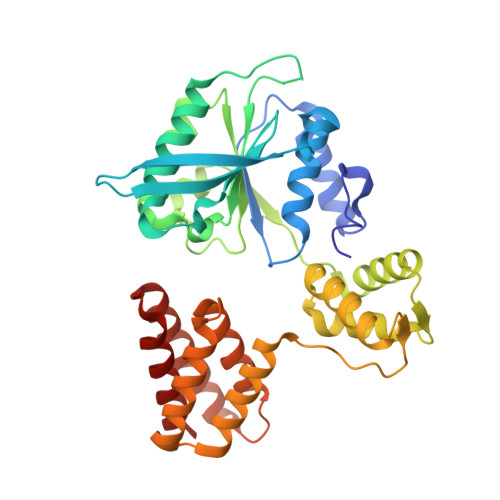
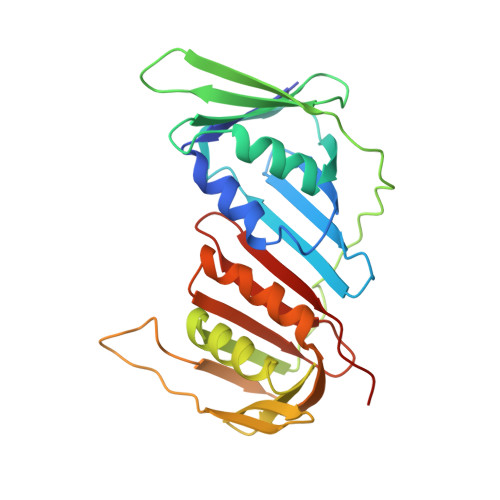
Sliding clamps are ring-shaped protein complexes that are integral to the DNA replication machinery of all life. Sliding clamps are opened and installed onto DNA by clamp loader AAA+ ATPase complexes. However, how a clamp loader opens and closes the sliding clamp around DNA is still unknown. Here, we describe structures of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae clamp loader Replication Factor C (RFC) bound to its cognate sliding clamp Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) en route to successful loading. RFC first binds to PCNA in a dynamic, closed conformation that blocks both ATPase activity and DNA binding. RFC then opens the PCNA ring through a large-scale 'crab-claw' expansion of both RFC and PCNA that explains how RFC prefers initial binding of PCNA over DNA. Next, the open RFC:PCNA complex binds DNA and interrogates the primer-template junction using a surprising base-flipping mechanism. Our structures indicate that initial PCNA opening and subsequent closure around DNA do not require ATP hydrolysis, but are driven by binding energy. ATP hydrolysis, which is necessary for RFC release, is triggered by interactions with both PCNA and DNA, explaining RFC's switch-like ATPase activity. Our work reveals how a AAA+ machine undergoes dramatic conformational changes for achieving binding preference and substrate remodeling.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biotechnology, University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: