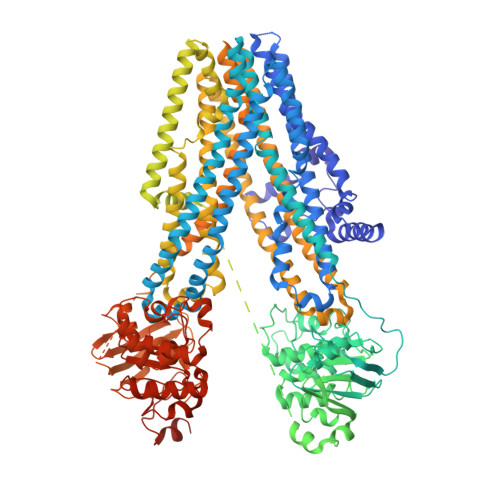
Mechanism of CFTR correction by type I folding correctors.
Fiedorczuk, K., Chen, J.(2022) Cell 185: 158-168.e11
- PubMed: 34995514
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SV7, 7SVD, 7SVR - PubMed Abstract:
Small molecule chaperones have been exploited as therapeutics for the hundreds of diseases caused by protein misfolding. The most successful examples are the CFTR correctors, which transformed cystic fibrosis therapy. These molecules revert folding defects of the ΔF508 mutant and are widely used to treat patients. To investigate the molecular mechanism of their action, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of CFTR in complex with the FDA-approved correctors lumacaftor or tezacaftor. Both drugs insert into a hydrophobic pocket in the first transmembrane domain (TMD1), linking together four helices that are thermodynamically unstable. Mutating residues at the binding site rendered ΔF508-CFTR insensitive to lumacaftor and tezacaftor, underscoring the functional significance of the structural discovery. These results support a mechanism in which the correctors stabilize TMD1 at an early stage of biogenesis, prevent its premature degradation, and thereby allosterically rescuing many disease-causing mutations.
- Laboratory of Membrane Biology and Biophysics, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY 10065, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: