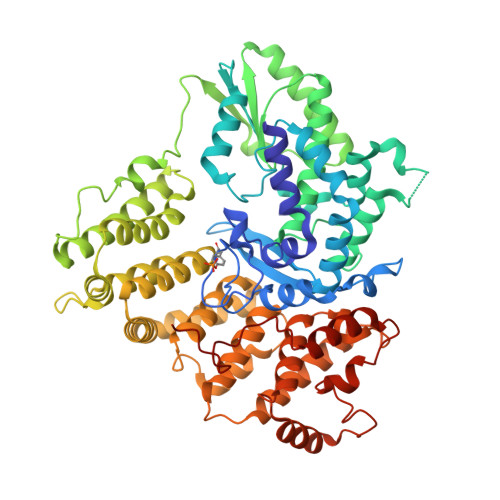
Mechanism of protein-primed template-independent DNA synthesis by Abi polymerases.
Figiel, M., Gapinska, M., Czarnocki-Cieciura, M., Zajko, W., Sroka, M., Skowronek, K., Nowotny, M.(2022) Nucleic Acids Res 50: 10026-10040
- PubMed: 36107766
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac772
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7R06, 7R07, 7R08, 7Z0Z - PubMed Abstract:
Abortive infection (Abi) is a bacterial antiphage defense strategy involving suicide of the infected cell. Some Abi pathways involve polymerases that are related to reverse transcriptases. They are unique in the way they combine the ability to synthesize DNA in a template-independent manner with protein priming. Here, we report crystal and cryo-electron microscopy structures of two Abi polymerases: AbiK and Abi-P2. Both proteins adopt a bilobal structure with an RT-like domain that comprises palm and fingers subdomains and a unique helical domain. AbiK and Abi-P2 adopt a hexameric and trimeric configuration, respectively, which is unprecedented for reverse transcriptases. Biochemical experiments showed that the formation of these oligomers is required for the DNA polymerization activity. The structure of the AbiK-DNA covalent adduct visualized interactions between the 3' end of DNA and the active site and covalent attachment of the 5' end of DNA to a tyrosine residue used for protein priming. Our data reveal a structural basis of the mechanism of highly unusual template-independent protein-priming polymerases.
- Laboratory of Protein Structure, International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, Warsaw, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: