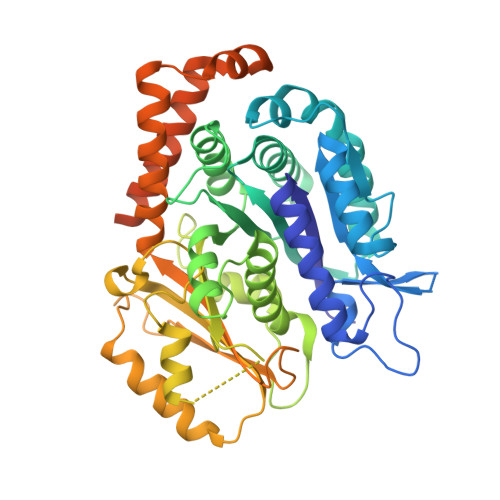
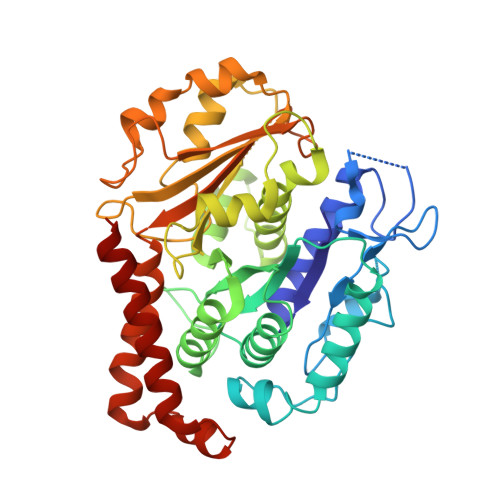
Diverse cytomotive actins and tubulins share a polymerization switch mechanism conferring robust dynamics.
Wagstaff, J.M., Planelles-Herrero, V.J., Sharov, G., Alnami, A., Kozielski, F., Derivery, E., Lowe, J.(2023) Sci Adv 9: eadf3021-eadf3021
- PubMed: 36989372
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adf3021
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QUC, 7QUD, 7QUP, 7QUQ - PubMed Abstract:
Protein filaments are used in myriads of ways to organize other molecules within cells. Some filament-forming proteins couple the hydrolysis of nucleotides to their polymerization cycle, thus powering the movement of other molecules. These filaments are termed cytomotive. Only members of the actin and tubulin protein superfamilies are known to form cytomotive filaments. We examined the basis of cytomotivity via structural studies of the polymerization cycles of actin and tubulin homologs from across the tree of life. We analyzed published data and performed structural experiments designed to disentangle functional components of these complex filament systems. Our analysis demonstrates the existence of shared subunit polymerization switches among both cytomotive actins and tubulins, i.e., the conformation of subunits switches upon assembly into filaments. These cytomotive switches can explain filament robustness, by enabling the coupling of kinetic and structural polarities required for cytomotive behaviors and by ensuring that single cytomotive filaments do not fall apart.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: