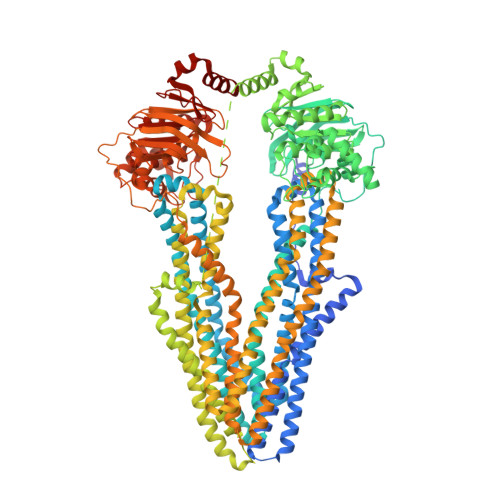
Structural and functional investigation of ABC transporter STE6-2p from Pichia pastoris reveals unexpected interaction with sterol molecules.
Schleker, E.S.M., Buschmann, S., Xie, H., Welsch, S., Michel, H., Reinhart, C.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2202822119-e2202822119
- PubMed: 36256814
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2202822119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QKR, 7QKS - PubMed Abstract:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are multidomain transmembrane proteins, which facilitate the transport of various substances across cell membranes using energy derived from ATP hydrolysis. They are important drug targets since they mediate decreased drug susceptibility during pharmacological treatments. For the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris , a model organism that is a widely used host for protein expression, the role and function of its ABC transporters is unexplored. In this work, we investigated the Pichia ABC-B transporter STE6-2p. Functional investigations revealed that STE6-2p is capable of transporting rhodamines in vivo and is active in the presence of verapamil and triazoles in vitro. A phylogenetic analysis displays homology among multidrug resistance (MDR) transporters from pathogenic fungi to human ABC-B transporters. Further, we present high-resolution single-particle electron cryomicroscopy structures of an ABC transporter from P. pastoris in the apo conformation (3.1 Å) and in complex with verapamil and adenylyl imidodiphosphate (AMP-PNP) (3.2 Å). An unknown density between transmembrane helices 4, 5, and 6 in both structures suggests the presence of a sterol-binding site of unknown function.
- Department of Molecular Membrane Biology, Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, D-60438 Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: