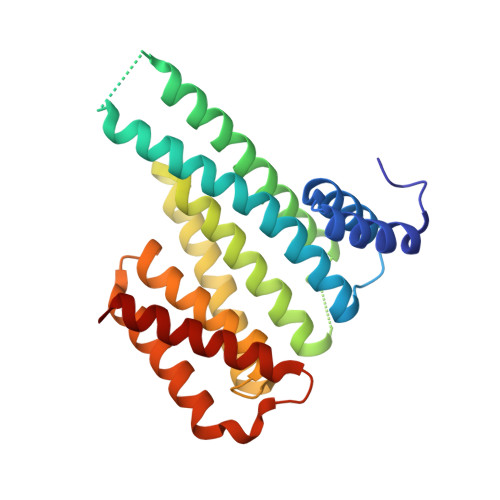
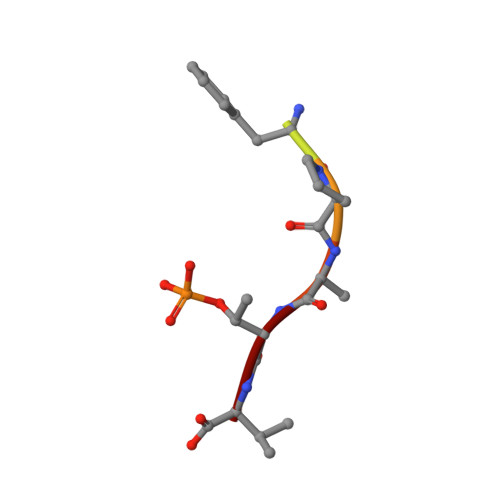
Designing Selective Drug-like Molecular Glues for the Glucocorticoid Receptor/14-3-3 Protein-Protein Interaction.
Pallesen, J.S., Munier, C.C., Bosica, F., Andrei, S.A., Edman, K., Gunnarsson, A., La Sala, G., Putra, O.D., Srdanovic, S., Wilson, A.J., Wissler, L., Ottmann, C., Perry, M.W.D., O'Mahony, G.(2022) J Med Chem 65: 16818-16828
- PubMed: 36484727
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01635
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7PWT, 7PWZ, 8A9G - PubMed Abstract:
The ubiquitously expressed glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a nuclear receptor that controls a broad range of biological processes and is activated by steroidal glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone or dexamethasone. Glucocorticoids are used to treat a wide variety of conditions, from inflammation to cancer but suffer from a range of side effects that motivate the search for safer GR modulators. GR is also regulated outside the steroid-binding site through protein-protein interactions (PPIs) with 14-3-3 adapter proteins. Manipulation of these PPIs will provide insights into noncanonical GR signaling as well as a new level of control over GR activity. We report the first molecular glues that selectively stabilize the 14-3-3/GR PPI using the related nuclear receptor estrogen receptor α (ERα) as a selectivity target to drive design. These 14-3-3/GR PPI stabilizers can be used to dissect noncanonical GR signaling and enable the development of novel atypical GR modulators.
- Medicinal Chemistry, Research and Early Development, Cardiovascular, Renal and Metabolism, Biopharmaceuticals R&D, AstraZeneca, Pepparedsleden 1, 43183 Mölndal, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: