Structural Insight into a Yeast Maltase-The Ba AG2 from Blastobotrys adeninivorans with Transglycosylating Activity.
Ernits, K., Kjeldsen, C., Persson, K., Grigor, E., Alamae, T., Visnapuu, T.(2021) J Fungi (Basel) 7
- PubMed: 34682239
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100816
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7P01, 7P07 - PubMed Abstract:
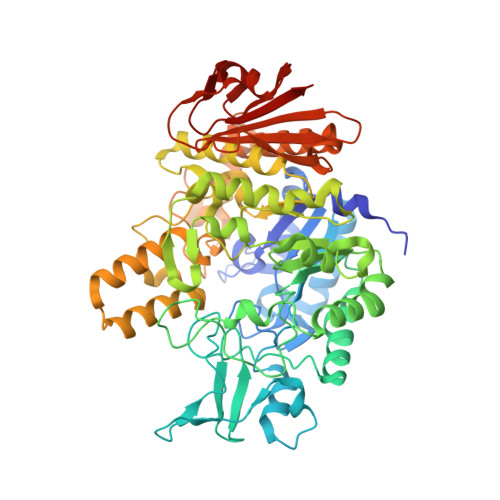
An early-diverged yeast, Blastobotrys ( Arxula ) adeninivorans ( Ba ), has biotechnological potential due to nutritional versatility, temperature tolerance, and production of technologically applicable enzymes. We have biochemically characterized from the Ba type strain (CBS 8244) the GH13-family maltase Ba AG2 with efficient transglycosylation activity on maltose. In the current study, transglycosylation of sucrose was studied in detail. The chemical entities of sucrose-derived oligosaccharides were determined using nuclear magnetic resonance. Several potentially prebiotic oligosaccharides with α-1,1, α-1,3, α-1,4, and α-1,6 linkages were disclosed among the products. Trisaccharides isomelezitose, erlose, and theanderose, and disaccharides maltulose and trehalulose were dominant transglycosylation products. To date no structure for yeast maltase has been determined. Structures of the Ba AG2 with acarbose and glucose in the active center were solved at 2.12 and 2.13 Å resolution, respectively. Ba AG2 exhibited a catalytic domain with a (β/α) 8 -barrel fold and Asp216, Glu274, and Asp348 as the catalytic triad. The fairly wide active site cleft contained water channels mediating substrate hydrolysis. Next to the substrate-binding pocket an enlarged space for potential binding of transglycosylation acceptors was identified. The involvement of a Glu (Glu309) at subsite +2 and an Arg (Arg233) at subsite +3 in substrate binding was shown for the first time for α-glucosidases.
- Department of Chemistry, Umeå University, 90187 Umeå, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: