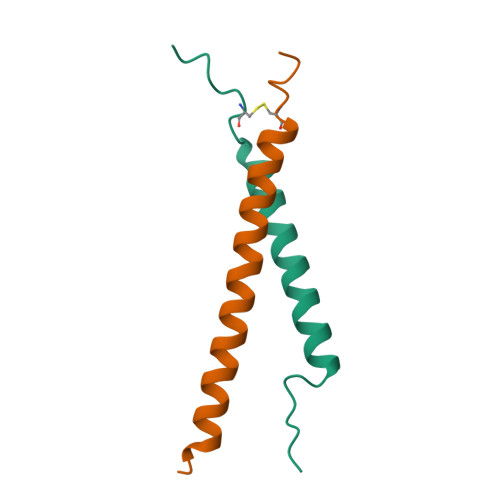
Insight Into Pathological Integrin alpha IIb beta 3 Activation From Safeguarding The Inactive State.
Situ, A.J., Kim, J., An, W., Kim, C., Ulmer, T.S.(2021) J Mol Biology 433: 166832-166832
- PubMed: 33539882
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166832
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KN0 - PubMed Abstract:
The inhibition of physiological activation pathways of the platelet adhesion receptor integrin αIIbβ3 may fail to prevent fatal thrombosis, suggesting that the receptor is at risk of activation by yet an unidentified pathway. Here, we report the discovery and characterization of a structural motif that safeguards the receptor by selectively destabilizing its inactive state. At the extracellular membrane border, an overpacked αIIb(W968)-β3(I693) contact prevents αIIb(Gly972) from optimally assembling the αIIbβ3 transmembrane complex, which maintains the inactive state. This destabilization of approximately 1.0 kcal/mol could be mitigated by hydrodynamic forces but not physiological agonists, thereby identifying hydrodynamic forces as pathological activation stimulus. As reproductive life spans are not generally limited by cardiovascular disease, it appears that the evolution of the safeguard was driven by fatal, hydrodynamic force-mediated integrin αIIbβ3 activation in the healthy cardiovascular system. The triggering of the safeguard solely by pathological stimuli achieves an effective increase of the free energy barrier between inactive and active receptor states without incurring an increased risk of bleeding. Thus, integrin αIIbβ3 has evolved an effective way to protect receptor functional states that indicates the availability of a mechanical activation pathway when hydrodynamic forces exceed physiological margins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology and Neuroscience, Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.