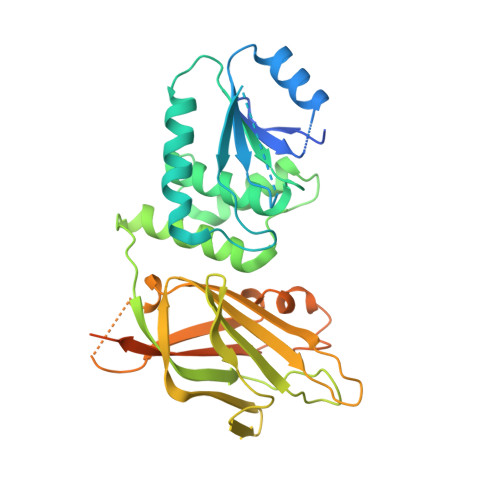
The structural basis of PTEN regulation by multi-site phosphorylation.
Dempsey, D.R., Viennet, T., Iwase, R., Park, E., Henriquez, S., Chen, Z., Jeliazkov, J.R., Palanski, B.A., Phan, K.L., Coote, P., Gray, J.J., Eck, M.J., Gabelli, S.B., Arthanari, H., Cole, P.A.(2021) Nat Struct Mol Biol 28: 858-868
- PubMed: 34625746
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00668-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JTX, 7JUK, 7JUL, 7JVX - PubMed Abstract:
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP 3 ) phospholipid phosphatase that is commonly mutated or silenced in cancer. PTEN's catalytic activity, cellular membrane localization and stability are orchestrated by a cluster of C-terminal phosphorylation (phospho-C-tail) events on Ser380, Thr382, Thr383 and Ser385, but the molecular details of this multi-faceted regulation have remained uncertain. Here we use a combination of protein semisynthesis, biochemical analysis, NMR, X-ray crystallography and computational simulations on human PTEN and its sea squirt homolog, VSP, to obtain a detailed picture of how the phospho-C-tail forms a belt around the C2 and phosphatase domains of PTEN. We also visualize a previously proposed dynamic N-terminal α-helix and show that it is key for PTEN catalysis but disordered upon phospho-C-tail interaction. This structural model provides a comprehensive framework for how C-tail phosphorylation can impact PTEN's cellular functions.
- Division of Genetics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: