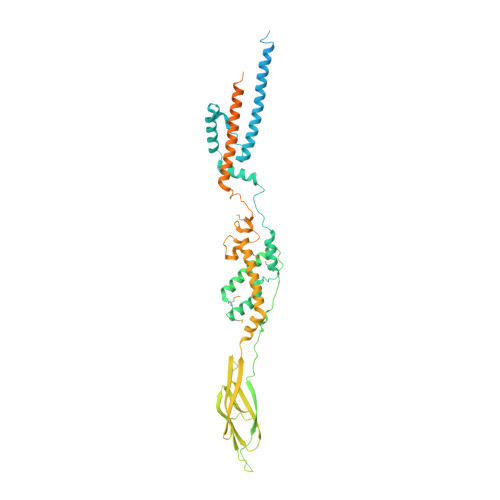
Structure of the Extracellular Region of the Bacterial Type VIIb Secretion System Subunit EsaA.
Klein, T.A., Grebenc, D.W., Gandhi, S.Y., Shah, V.S., Kim, Y., Whitney, J.C.(2021) Structure 29: 177-185.e6
- PubMed: 33238147
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.11.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JQE - PubMed Abstract:
Gram-positive bacteria use type VII secretion systems (T7SSs) to export effector proteins that manipulate the physiology of nearby prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Several mycobacterial T7SSs have established roles in virulence. By contrast, the genetically distinct T7SSb pathway found in Firmicutes bacteria more often functions to mediate bacterial competition. A lack of structural information on the T7SSb has limited the understanding of effector export by this protein secretion apparatus. Here, we present the 2.4 Å crystal structure of the extracellular region of the T7SSb subunit EsaA from Streptococcus gallolyticus. Our structure reveals that homodimeric EsaA is an elongated, arrow-shaped protein with a surface-accessible "tip", which in some species of bacteria serves as a receptor for lytic bacteriophages. Because it is the only T7SSb subunit large enough to traverse the peptidoglycan layer of Firmicutes, we propose that EsaA plays a critical role in transporting effectors across the entirety of the Gram-positive cell envelope.
- Michael DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON L8S 4K1, Canada; Department of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON L8S 4K1, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: