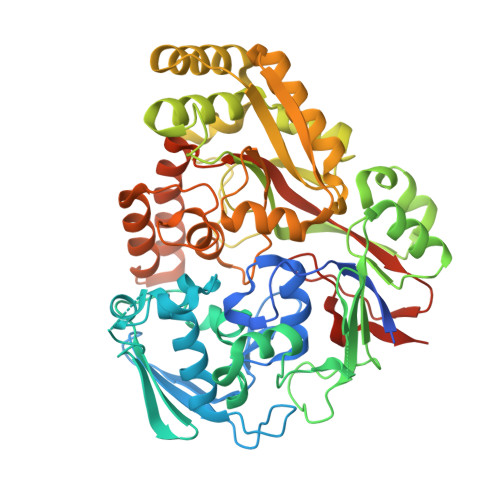
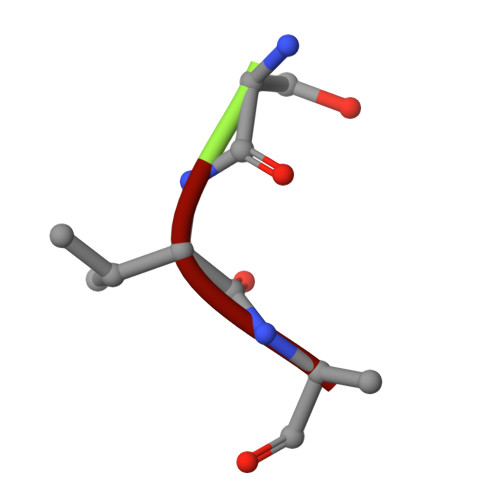
Biophysical analysis of the Mycobacteria tuberculosis peptide binding protein DppA reveals a stringent peptide binding pocket.
Fernando, D.M., Gee, C.T., Griffith, E.C., Meyer, C.J., Wilt, L.A., Tangallapally, R., Wallace, M.J., Miller, D.J., Lee, R.E.(2021) Tuberculosis (Edinb) 132: 102157-102157
- PubMed: 34894561
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2021.102157
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JLS - PubMed Abstract:
The peptide binding protein DppA is an ABC transporter found in prokaryotes that has the potential to be used as drug delivery tool for hybrid antibiotic compounds. Understanding the motifs and structures that bind to DppA is critical to the development of these bivalent compounds. This study focused on the biophysical analysis of the MtDppA from M. tuberculosis. Analysis of the crystal structure revealed a SVA tripeptide was co-crystallized with the protein. Further peptide analysis demonstrated MtDppA shows very little affinity for dipeptides but rather preferentially binds to peptides that are 3-4 amino acids in length. The structure-activity relationships (SAR) between MtDppA and tripeptides with varied amino acid substitutions were evaluated using thermal shift, SPR, and molecular dynamics simulations. Efforts to identify novel ligands for use as alternative scaffolds through the thermal shift screening of 35,000 compounds against MtDppA were unsuccessful, indicating that the MtDppA binding pocket is highly specialized for uptake of peptides. Future development of compounds that seek to utilize MtDppA as a drug delivery mechanism, will likely require a tri- or tetrapeptide component with a hydrophobic -non-acidic peptide sequence.
- Department of Chemical Biology and Therapeutics, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN 38105, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: