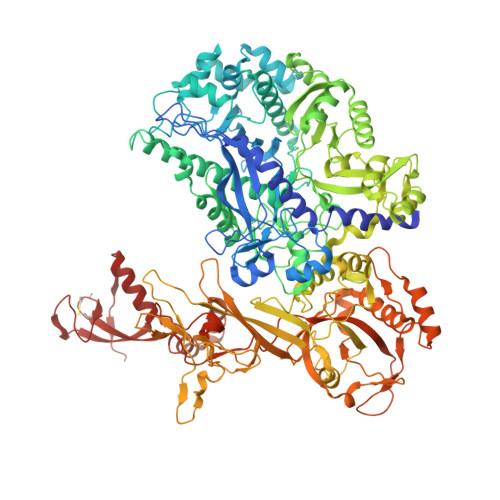
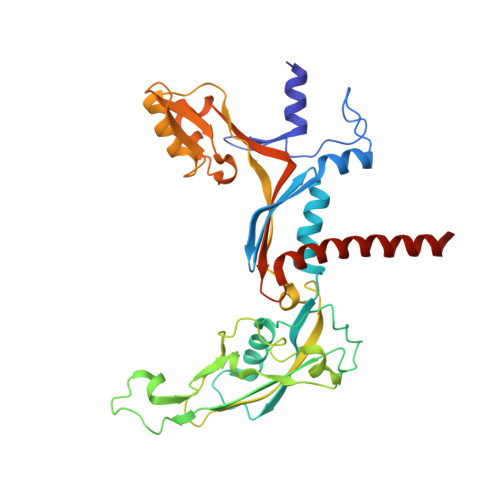
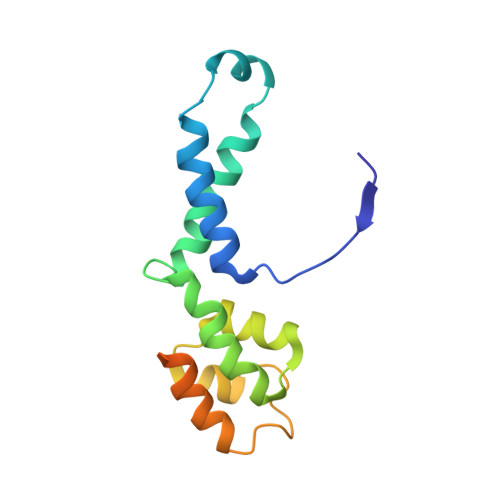
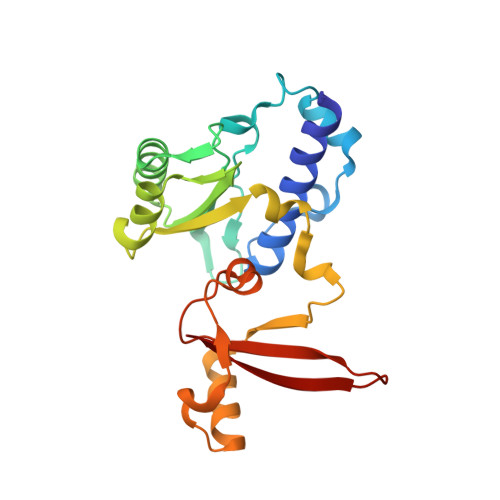
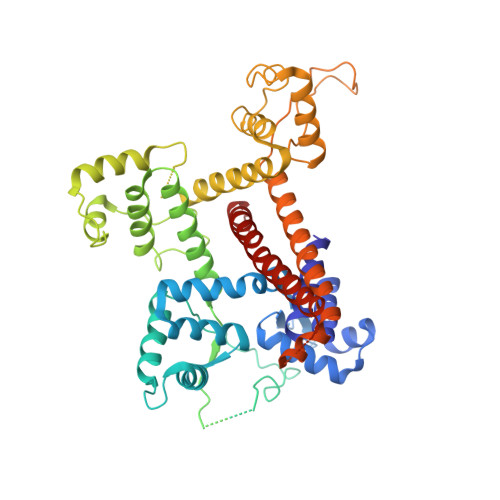
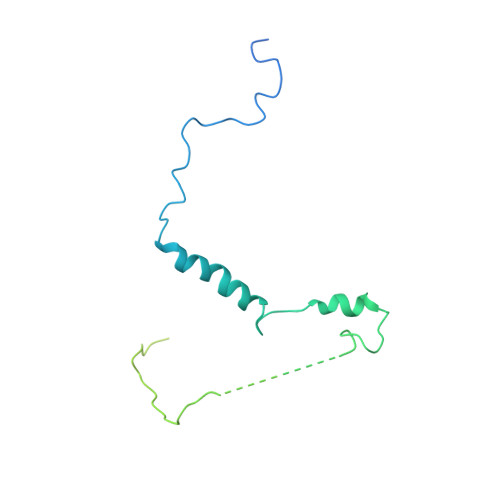
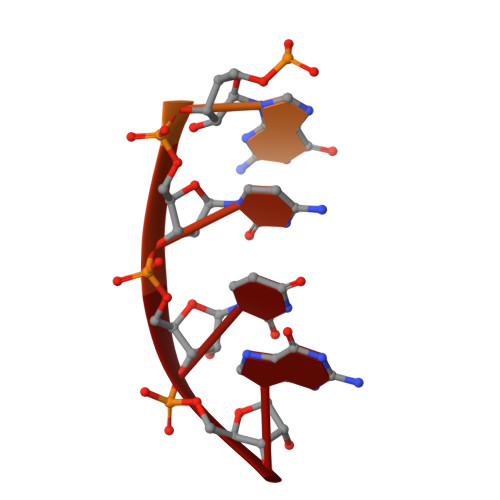
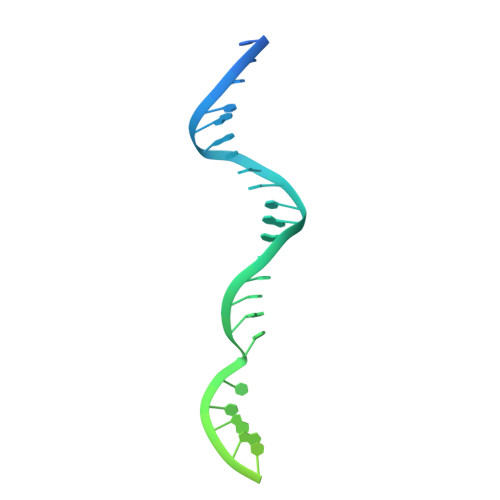
Structural insights into RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription termination through trapping poly-deoxythymidine.
Hou, H., Li, Y., Wang, M., Liu, A., Yu, Z., Chen, K., Zhao, D., Xu, Y.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 6135-6135
- PubMed: 34675218
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26402-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7FJI, 7FJJ - PubMed Abstract:
Termination of the RNA polymerase III (Pol III)-mediated transcription requires the conversion of an elongation complex (EC) to a pre-termination complex (PTC) on poly-deoxythymidine (dT)-containing non-template strand, a mechanism distinct from Pol I and Pol II. Here, our in vitro transcription elongation assay showed that 5-7 dT-containing DNA template led to transcription termination of Pol III, but not Pol I or Pol II. We assembled human Pol III PTC on a 7 dT-containing DNA template and determined the structure at 3.6 Å resolution. The structure reveals that poly-dT are trapped in a narrow exit tunnel formed by RPC2. A hydrophobic gate of the exit tunnel separates the bases of two connected deoxythymidines and may prevent translocation of the non-template strand. The fork loop 2 stabilizes both template and non-template strands around the transcription fork, and may further prevent strand translocation. Our study shows that the Pol III-specific exit tunnel and FL2 allow for efficient translocation of non-poly-dT sequence during transcription elongation but trap poly-dT to promote DNA retention of Pol III, revealing molecular mechanism of poly-dT-dependent transcription termination of Pol III.
- Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Radiation Oncology, and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Medical Epigenetics, Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University, Shanghai, 200032, China.
Organizational Affiliation: