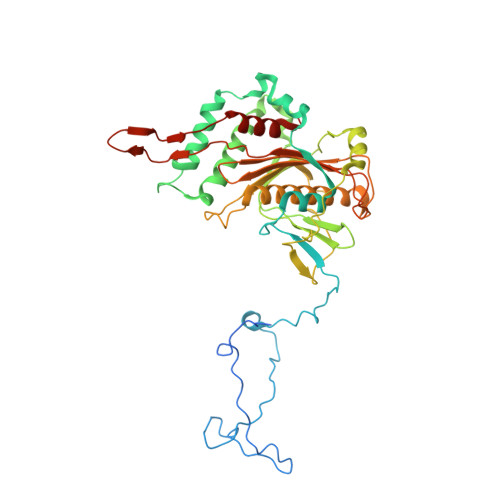
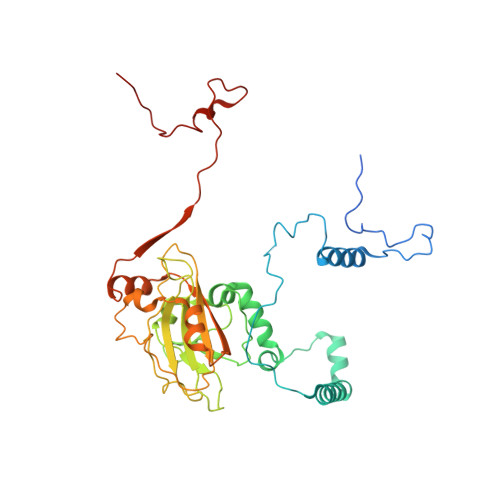
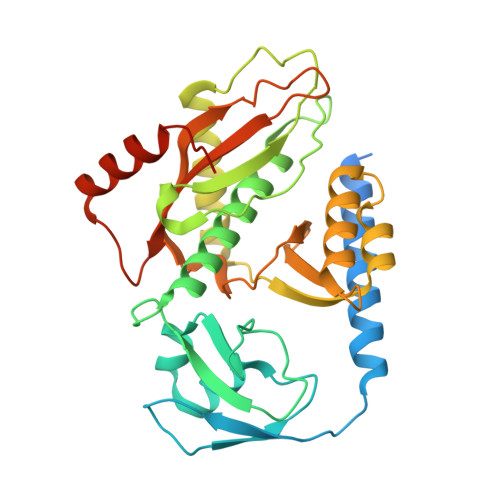
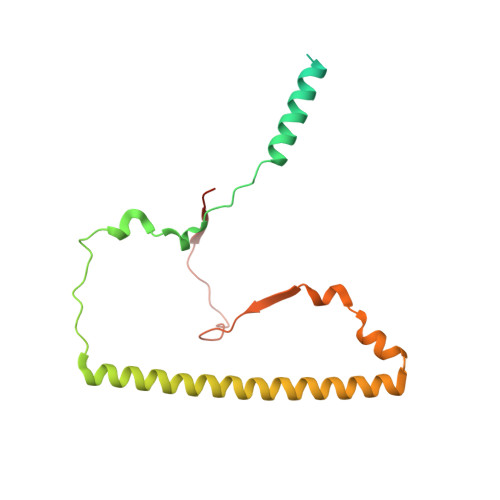
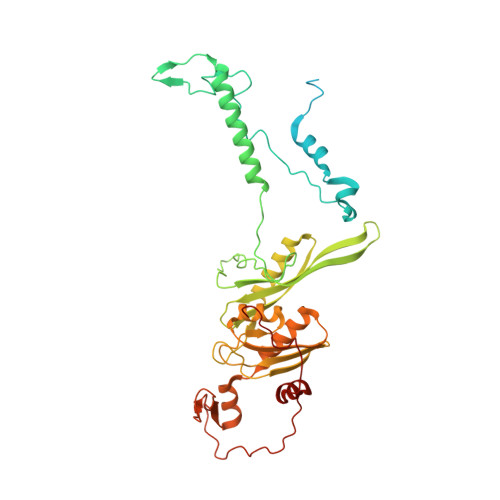
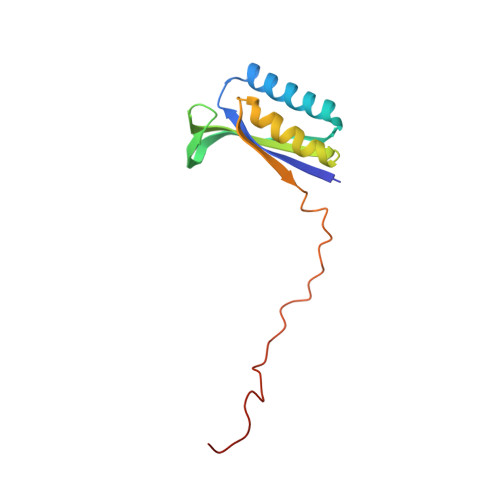
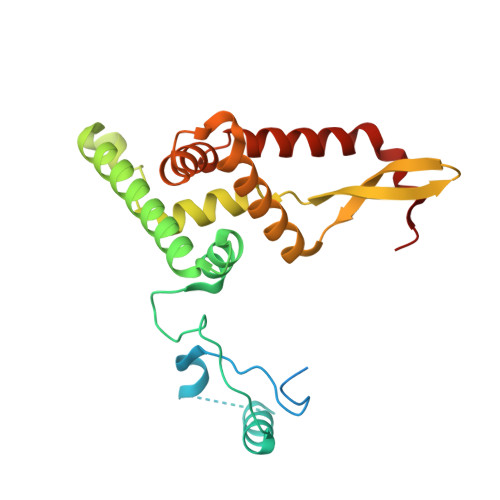
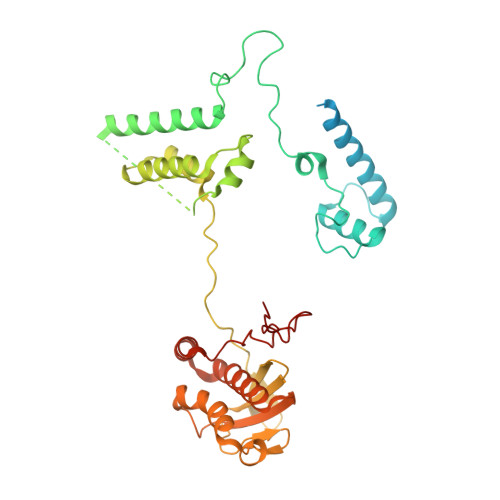
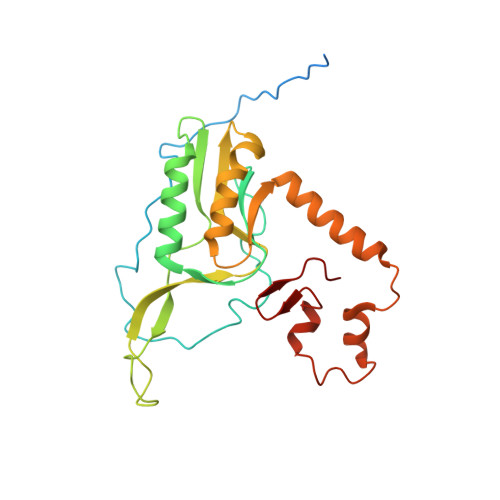
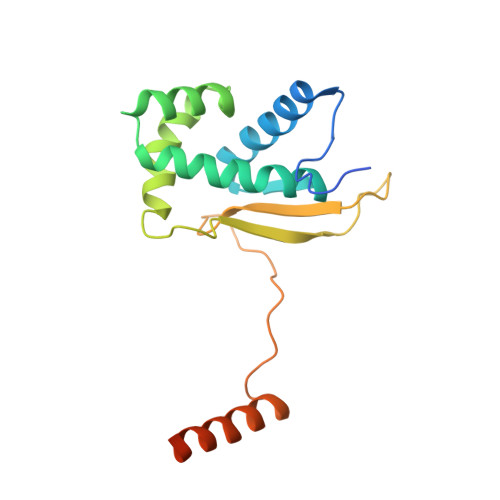
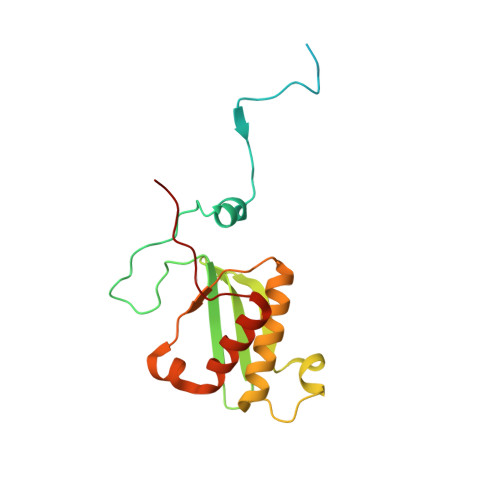
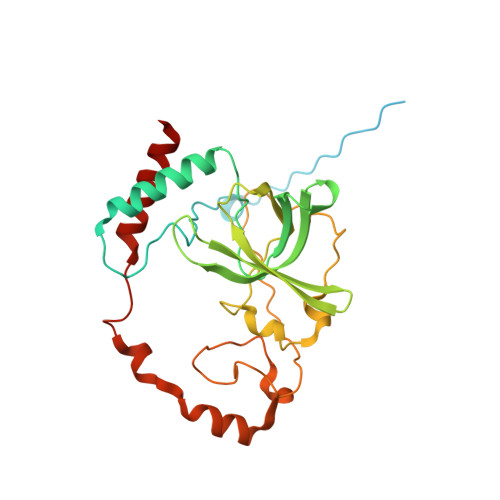
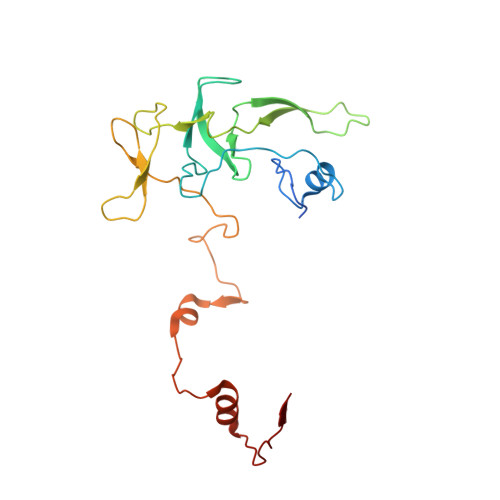
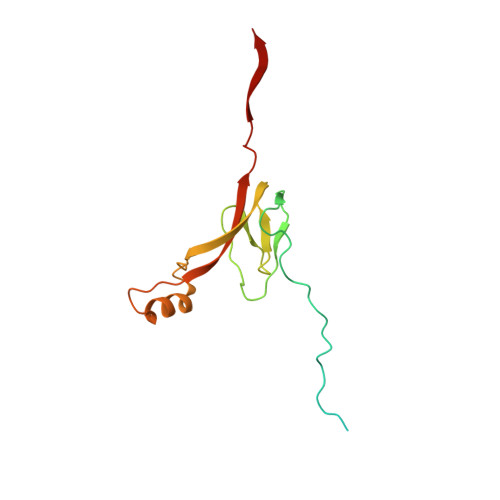
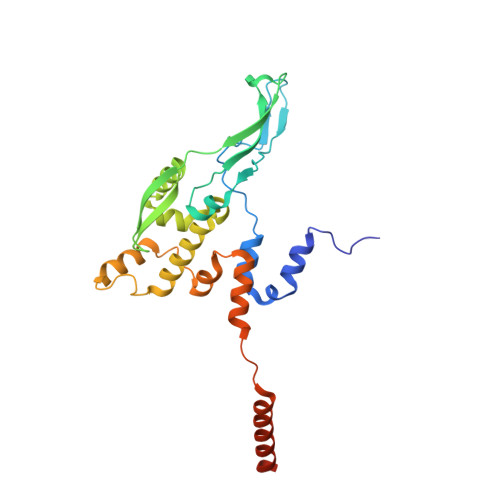
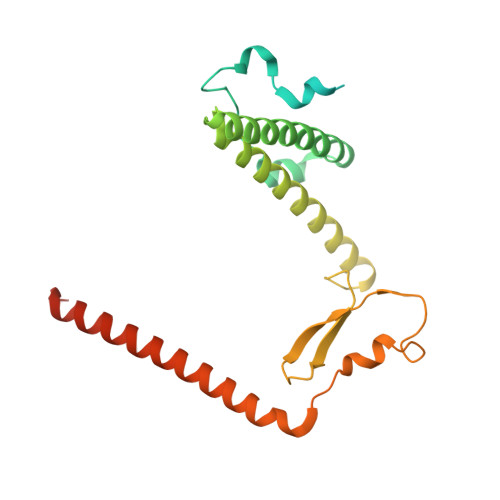
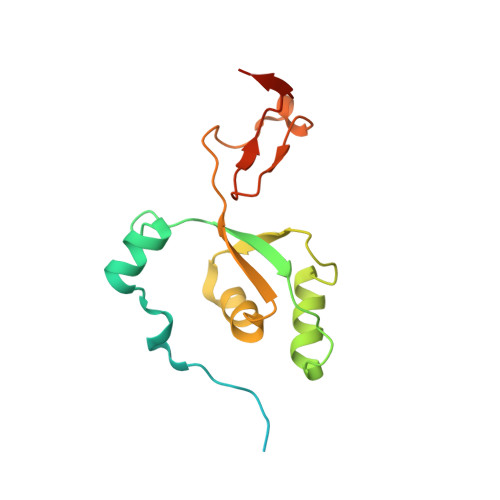
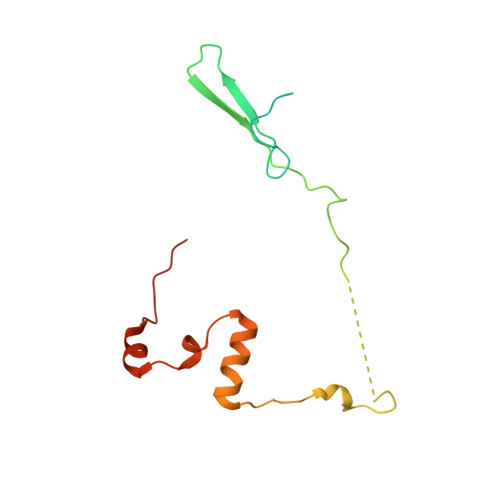
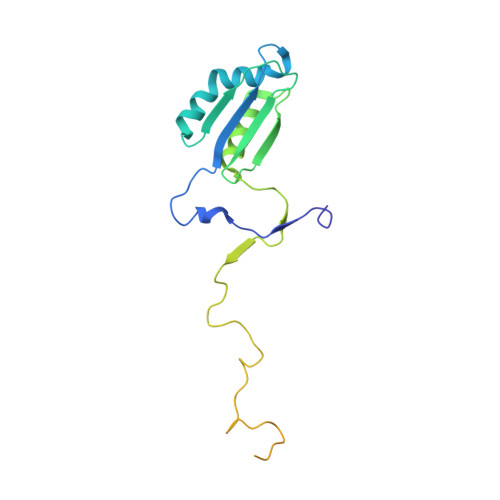
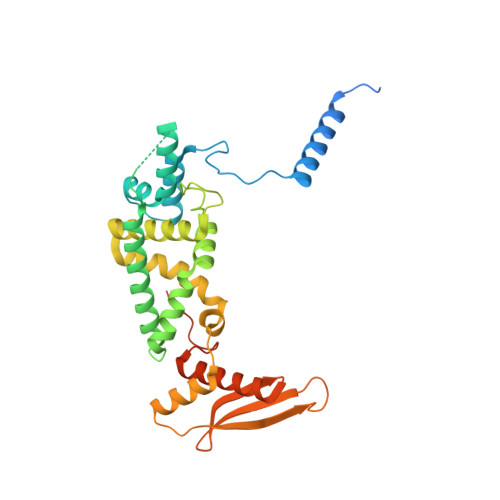
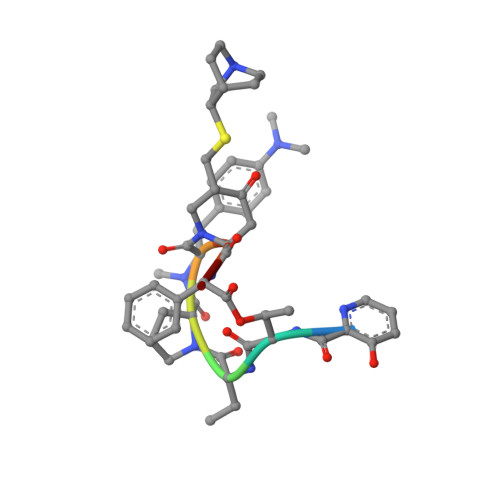
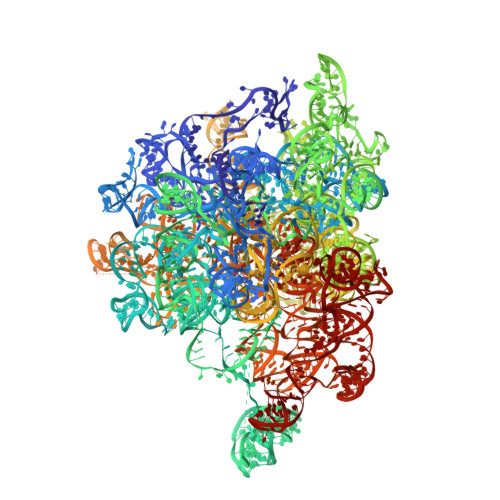
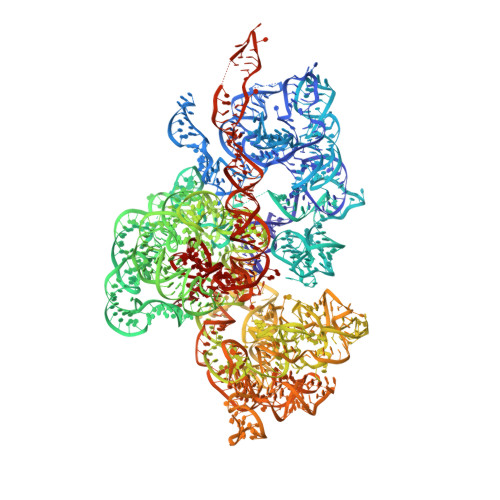
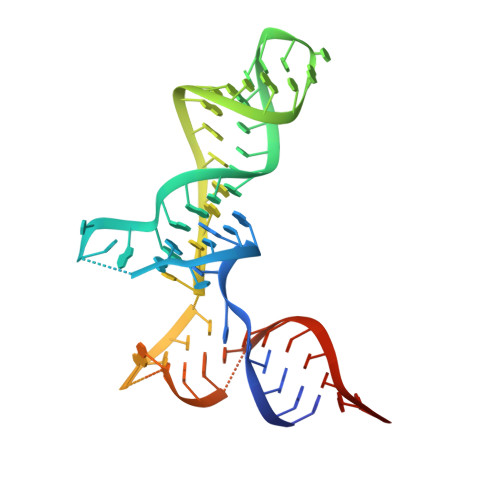
Structural basis of mitochondrial translation.
Aibara, S., Singh, V., Modelska, A., Amunts, A.(2020) Elife 9
- PubMed: 32812867
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.58362
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZS9, 6ZSA, 6ZSB, 6ZSC, 6ZSD, 6ZSE, 6ZSG, 7OG4 - PubMed Abstract:
Translation of mitochondrial messenger RNA (mt-mRNA) is performed by distinct mitoribosomes comprising at least 36 mitochondria-specific proteins. How these mitoribosomal proteins assist in the binding of mt-mRNA and to what extent they are involved in the translocation of transfer RNA (mt-tRNA) is unclear. To visualize the process of translation in human mitochondria, we report ~3.0 Å resolution structure of the human mitoribosome, including the L7/L12 stalk, and eight structures of its functional complexes with mt-mRNA, mt-tRNAs, recycling factor and additional trans factors. The study reveals a transacting protein module LRPPRC-SLIRP that delivers mt-mRNA to the mitoribosomal small subunit through a dedicated platform formed by the mitochondria-specific protein mS39. Mitoribosomal proteins of the large subunit mL40, mL48, and mL64 coordinate translocation of mt-tRNA. The comparison between those structures shows dynamic interactions between the mitoribosome and its ligands, suggesting a sequential mechanism of conformational changes.
- Science for Life Laboratory, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University, Solna, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: