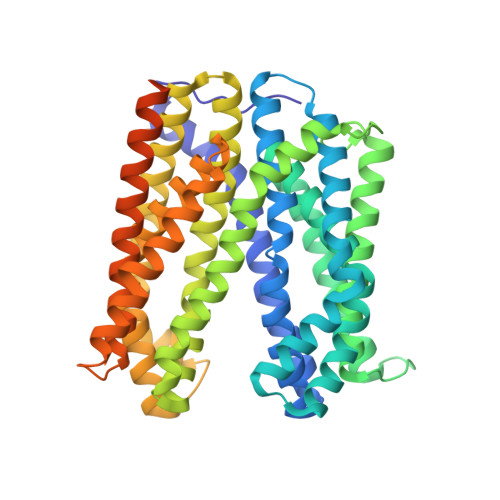
The structure of the Aquifex aeolicus MATE family multidrug resistance transporter and sequence comparisons suggest the existence of a new subfamily.
Zhao, J., Xie, H., Mehdipour, A.R., Safarian, S., Ermler, U., Munke, C., Thielmann, Y., Hummer, G., Ebersberger, I., Wang, J., Michel, H.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 34753818
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2107335118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Z70, 6Z71 - PubMed Abstract:
Multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporters are widespread in all domains of life. Bacterial MATE transporters confer multidrug resistance by utilizing an electrochemical gradient of H + or Na + to export xenobiotics across the membrane. Despite the availability of X-ray structures of several MATE transporters, a detailed understanding of the transport mechanism has remained elusive. Here we report the crystal structure of a MATE transporter from Aquifex aeolicus at 2.0-Å resolution. In light of its phylogenetic placement outside of the diversity of hitherto-described MATE transporters and the lack of conserved acidic residues, this protein may represent a subfamily of prokaryotic MATE transporters, which was proven by phylogenetic analysis. Furthermore, the crystal structure and substrate docking results indicate that the substrate binding site is located in the N bundle. The importance of residues surrounding this binding site was demonstrated by structure-based site-directed mutagenesis. We suggest that Aq_128 is functionally similar but structurally diverse from DinF subfamily transporters. Our results provide structural insights into the MATE transporter, which further advances our global understanding of this important transporter family.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory for Chemical Engineering, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Chemical Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, 300072 Tianjin, P. R. China.