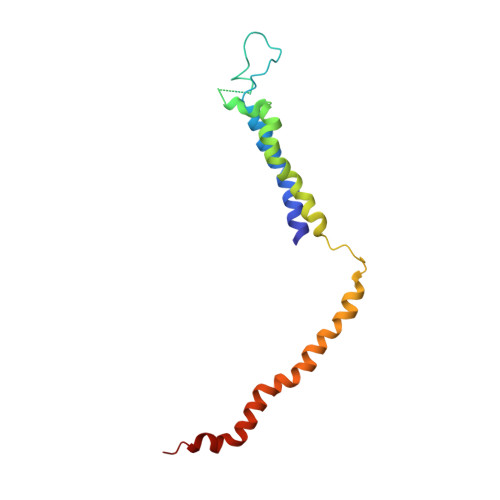
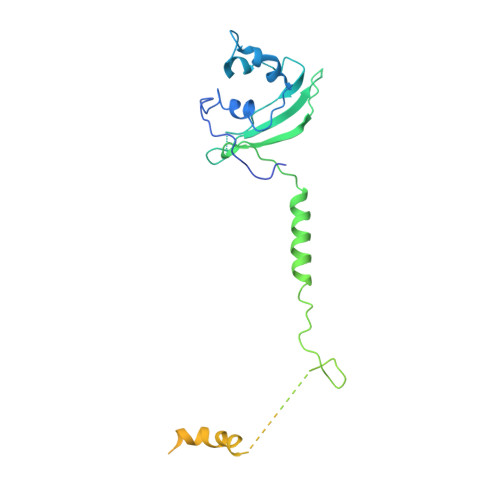
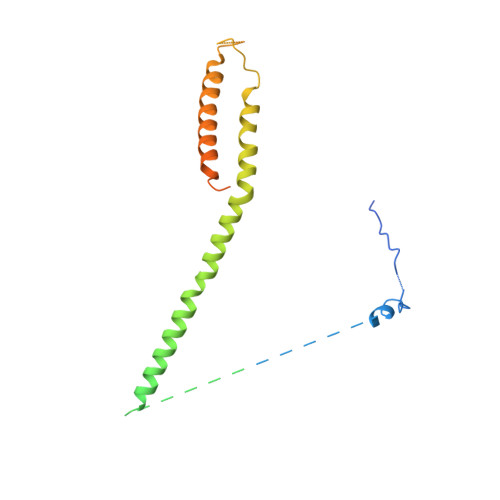
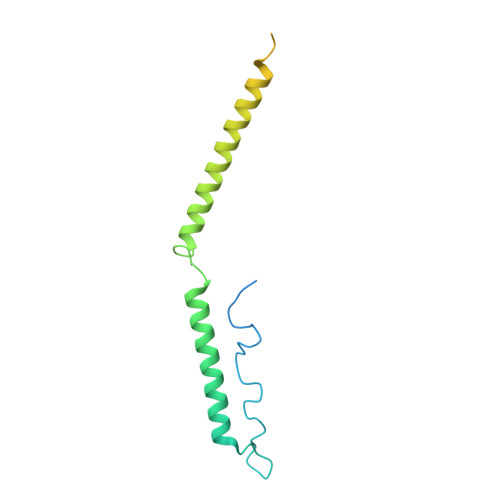
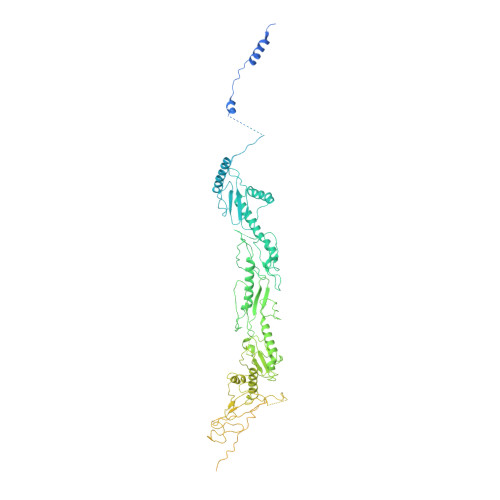
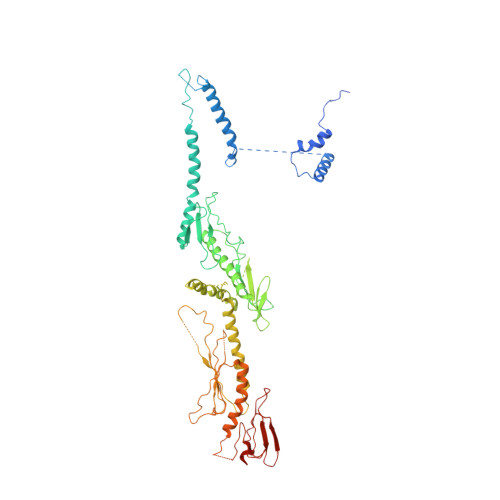
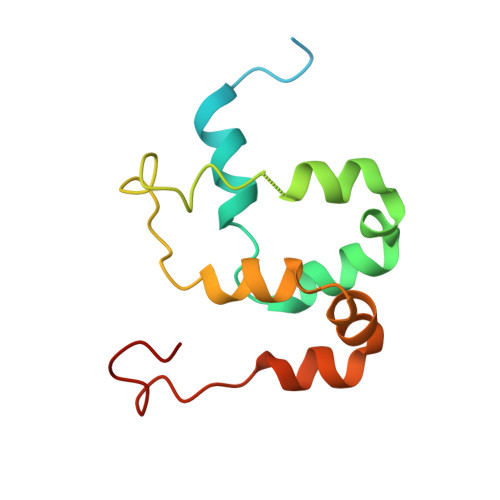
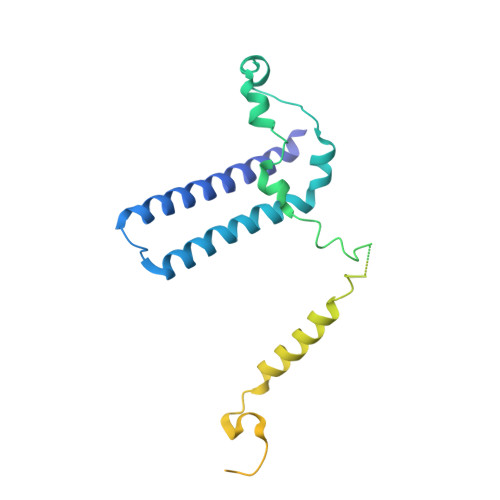
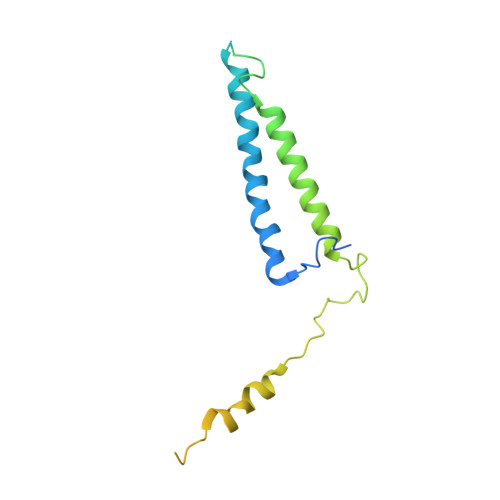
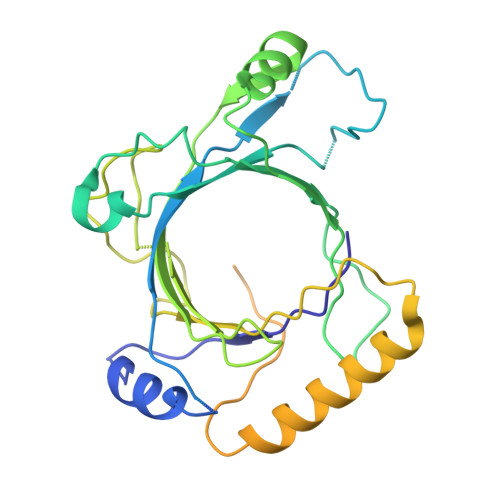
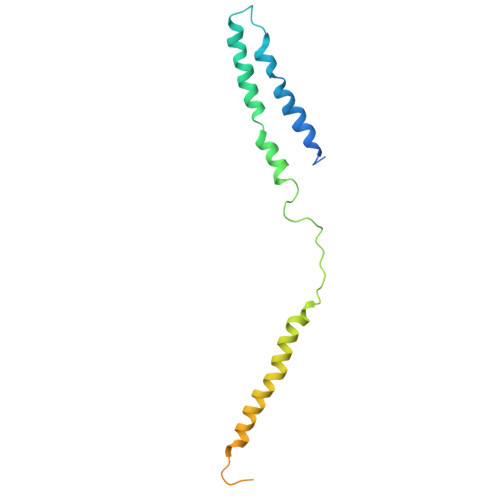
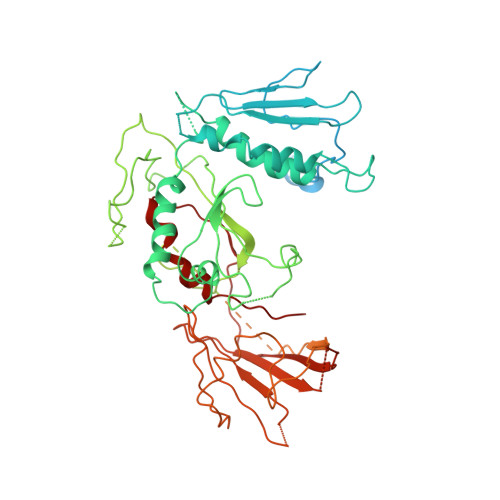
Mediator structure and conformation change.
Zhang, H., Chen, D.H., Mattoo, R.U.H., Bushnell, D.A., Wang, Y., Yuan, C., Wang, L., Wang, C., Davis, R.E., Nie, Y., Kornberg, R.D.(2021) Mol Cell 81: 1781-1788.e4
- PubMed: 33571424
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XP5, 7JMN - PubMed Abstract:
Mediator is a universal adaptor for transcription control. It serves as an interface between gene-specific activator or repressor proteins and the general RNA polymerase II (pol II) transcription machinery. Previous structural studies revealed a relatively small part of Mediator and none of the gene activator-binding regions. We have determined the cryo-EM structure of the Mediator at near-atomic resolution. The structure reveals almost all amino acid residues in ordered regions, including the major targets of activator proteins, the Tail module, and the Med1 subunit of the Middle module. Comparison of Mediator structures with and without pol II reveals conformational changes that propagate across the entire Mediator, from Head to Tail, coupling activator- and pol II-interacting regions.
- Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies, ShanghaiTech University, 201210 Shanghai, China; Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: