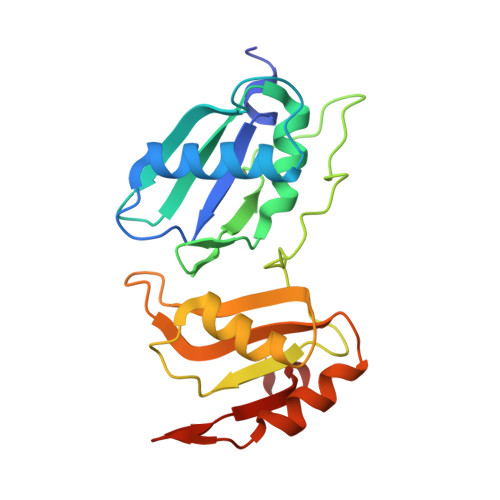
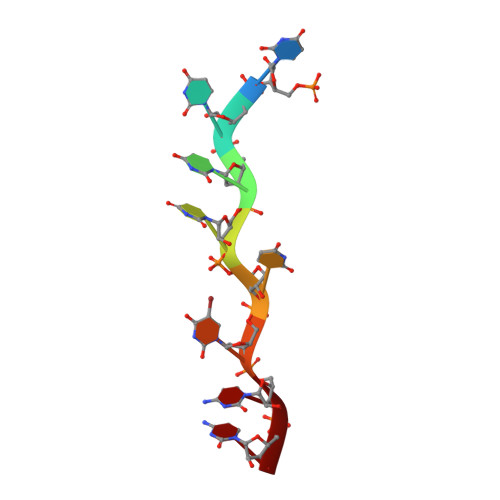
Representative cancer-associated U2AF2 mutations alter RNA interactions and splicing.
Maji, D., Glasser, E., Henderson, S., Galardi, J., Pulvino, M.J., Jenkins, J.L., Kielkopf, C.L.(2020) J Biological Chem 295: 17148-17157
- PubMed: 33020180
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015339
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XLV, 6XLW, 6XLX - PubMed Abstract:
High-throughput sequencing of hematologic malignancies and other cancers has revealed recurrent mis-sense mutations of genes encoding pre-mRNA splicing factors. The essential splicing factor U2AF2 recognizes a polypyrimidine-tract splice-site signal and initiates spliceosome assembly. Here, we investigate representative, acquired U2AF2 mutations, namely N196K or G301D amino acid substitutions associated with leukemia or solid tumors, respectively. We determined crystal structures of the wild-type (WT) compared with N196K- or G301D-substituted U2AF2 proteins, each bound to a prototypical AdML polypyrimidine tract, at 1.5, 1.4, or 1.7 Å resolutions. The N196K residue appears to stabilize the open conformation of U2AF2 with an inter-RNA recognition motif hydrogen bond, in agreement with an increased apparent RNA-binding affinity of the N196K-substituted protein. The G301D residue remains in a similar position as the WT residue, where unfavorable proximity to the RNA phosphodiester could explain the decreased RNA-binding affinity of the G301D-substituted protein. We found that expression of the G301D-substituted U2AF2 protein reduces splicing of a minigene transcript carrying prototypical splice sites. We further show that expression of either N196K- or G301D-substituted U2AF2 can subtly alter splicing of representative endogenous transcripts, despite the presence of endogenous, WT U2AF2 such as would be present in cancer cells. Altogether, our results demonstrate that acquired U2AF2 mutations such as N196K and G301D are capable of dysregulating gene expression for neoplastic transformation.
- Center for RNA Biology, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: