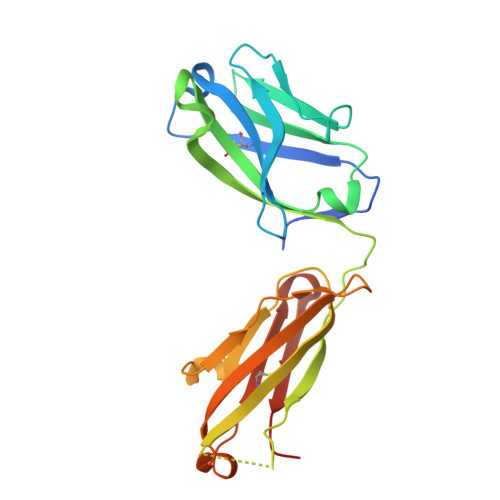
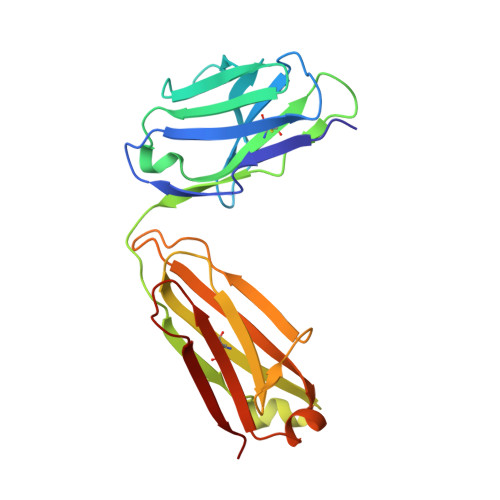
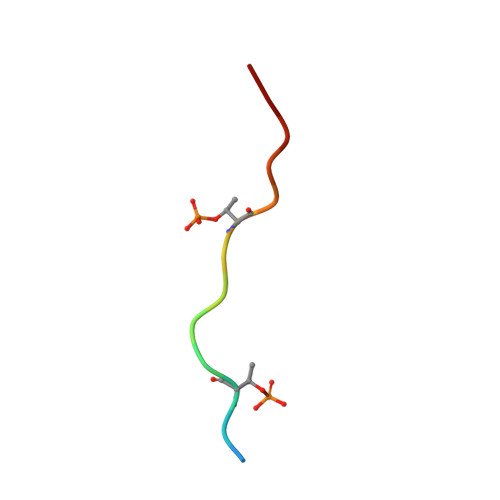
Discovery and Functional Characterization of hPT3, a Humanized Anti-Phospho Tau Selective Monoclonal Antibody.
Van Kolen, K., Malia, T.J., Theunis, C., Nanjunda, R., Teplyakov, A., Ernst, R., Wu, S.J., Luo, J., Borgers, M., Vandermeeren, M., Bottelbergs, A., Wintmolders, C., Lacy, E., Maurin, H., Larsen, P., Willems, R., Van De Casteele, T., Triana-Baltzer, G., Slemmon, R., Galpern, W., Trojanowski, J.Q., Sun, H., Mercken, M.H.(2020) J Alzheimers Dis 77: 1397-1416
- PubMed: 32894244
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-200544
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XLI - PubMed Abstract:
As a consequence of the discovery of an extracellular component responsible for the progression of tau pathology, tau immunotherapy is being extensively explored in both preclinical and clinical studies as a disease modifying strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Describe the characteristics of the anti-phospho (T212/T217) tau selective antibody PT3 and its humanized variant hPT3. By performing different immunization campaigns, a large collection of antibodies has been generated and prioritized. In depth, in vitro characterization using surface plasmon resonance, phospho-epitope mapping, and X-ray crystallography experiments were performed. Further characterization involved immunohistochemical staining on mouse- and human postmortem tissue and neutralization of tau seeding by immunodepletion assays. Various in vitro experiments demonstrated a high intrinsic affinity for PT3 and hPT3 for AD brain-derived paired helical filaments but also to non-aggregated phospho (T212/T217) tau. Further functional analyses in cellular and in vivo models of tau seeding demonstrated almost complete depletion of tau seeds in an AD brain homogenate. Ongoing trials will provide the clinical evaluation of the tau spreading hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease.
- Neuroscience Department, Janssen Research and Development, Beerse, Belgium.
Organizational Affiliation: