Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Stable Colchicine-Binding Site Tubulin Inhibitors 6-Aryl-2-benzoyl-pyridines as Potential Anticancer Agents.
Chen, H., Deng, S., Albadari, N., Yun, M.K., Zhang, S., Li, Y., Ma, D., Parke, D.N., Yang, L., Seagroves, T.N., White, S.W., Miller, D.D., Li, W.(2021) J Med Chem 64: 12049-12074
- PubMed: 34378386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00715
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
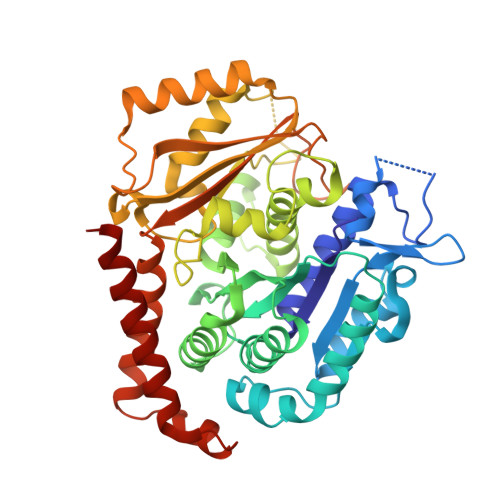
6XER, 6XES, 6XET - PubMed Abstract:
We previously reported a potent tubulin inhibitor CH-2-77. In this study, we optimized the structure of CH-2-77 by blocking metabolically labile sites and synthesized a series of CH-2-77 analogues. Two compounds, 40a and 60c , preserved the potency while improving the metabolic stability over CH-2-77 by 3- to 4-fold (46.8 and 29.4 vs 10.8 min in human microsomes). We determined the high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of 40a (resolution 2.3 Å) and 60c (resolution 2.6 Å) in complex with tubulin and confirmed their direct binding at the colchicine-binding site. In vitro , 60c maintained its mode of action by inhibiting tubulin polymerization and was effective against P-glycoprotein-mediated multiple drug resistance and taxol resistance. In vivo , 60c exhibited a strong inhibitory effect on tumor growth and metastasis in a taxol-resistant A375/TxR xenograft model without obvious toxicity. Collectively, this work showed that 60c is a promising lead compound for further development as a potential anticancer agent.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee 38163, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: