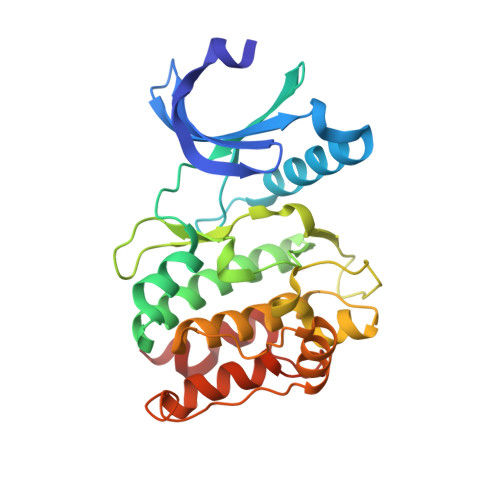
CaMKII binds both substrates and activators at the active site.
Ozden, C., Sloutsky, R., Mitsugi, T., Santos, N., Agnello, E., Gaubitz, C., Foster, J., Lapinskas, E., Esposito, E.A., Saneyoshi, T., Kelch, B.A., Garman, S.C., Hayashi, Y., Stratton, M.M.(2022) Cell Rep 40: 111064-111064
- PubMed: 35830796
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111064
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6X5G, 6X5Q, 7KL0, 7KL1, 7UIQ, 7UIR, 7UIS, 7UJP, 7UJQ, 7UJR, 7UJS, 7UJT - PubMed Abstract:
Ca 2+ /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a signaling protein required for long-term memory. When activated by Ca 2+ /CaM, it sustains activity even after the Ca 2+ dissipates. In addition to the well-known autophosphorylation-mediated mechanism, interaction with specific binding partners also persistently activates CaMKII. A long-standing model invokes two distinct S and T sites. If an interactor binds at the T-site, then it will preclude autoinhibition and allow substrates to be phosphorylated at the S site. Here, we specifically test this model with X-ray crystallography, molecular dynamics simulations, and biochemistry. Our data are inconsistent with this model. Co-crystal structures of four different activators or substrates show that they all bind to a single continuous site across the kinase domain. We propose a mechanistic model where persistent CaMKII activity is facilitated by high-affinity binding partners that kinetically compete with autoinhibition by the regulatory segment to allow substrate phosphorylation.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003, USA; Molecular and Cellular Biology Graduate Program, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: