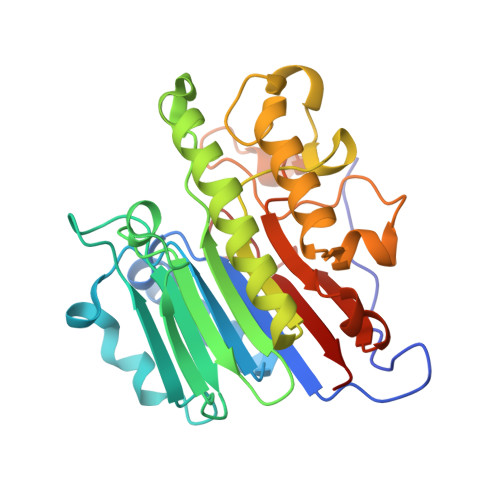
AP-endonuclease 1 sculpts DNA through an anchoring tyrosine residue on the DNA intercalating loop.
Hoitsma, N.M., Whitaker, A.M., Beckwitt, E.C., Jang, S., Agarwal, P.K., Van Houten, B., Freudenthal, B.D.(2020) Nucleic Acids Res 48: 7345-7355
- PubMed: 32542366
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa496
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6W4I, 6W4T - PubMed Abstract:
Base excision repair (BER) maintains genomic stability through the repair of DNA damage. Within BER, AP-endonuclease 1 (APE1) is a multifunctional enzyme that processes DNA intermediates through its backbone cleavage activity. To accomplish these repair activities, APE1 must recognize and accommodate several diverse DNA substrates. This is hypothesized to occur through a DNA sculpting mechanism where structural adjustments of the DNA substrate are imposed by the protein; however, how APE1 uniquely sculpts each substrate within a single rigid active site remains unclear. Here, we utilize structural and biochemical approaches to probe the DNA sculpting mechanism of APE1, specifically by characterizing a protein loop that intercalates the minor groove of the DNA (termed the intercalating loop). Pre-steady-state kinetics reveal a tyrosine residue within the intercalating loop (Y269) that is critical for AP-endonuclease activity. Using X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulations, we determined the Y269 residue acts to anchor the intercalating loop on abasic DNA. Atomic force microscopy reveals the Y269 residue is required for proper DNA bending by APE1, providing evidence for the importance of this mechanism. We conclude that this previously unappreciated tyrosine residue is key to anchoring the intercalating loop and stabilizing the DNA in the APE1 active site.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS 66160, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: