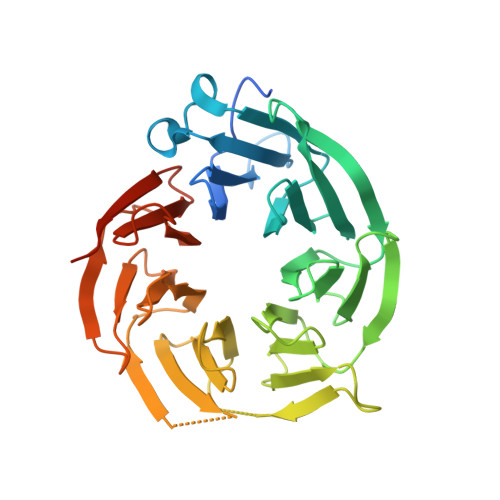
Molecular basis for substrate recruitment to the PRMT5 methylosome.
Mulvaney, K.M., Blomquist, C., Acharya, N., Li, R., Ranaghan, M.J., O'Keefe, M., Rodriguez, D.J., Young, M.J., Kesar, D., Pal, D., Stokes, M., Nelson, A.J., Jain, S.S., Yang, A., Mullin-Bernstein, Z., Columbus, J., Bozal, F.K., Skepner, A., Raymond, D., LaRussa, S., McKinney, D.C., Freyzon, Y., Baidi, Y., Porter, D., Aguirre, A.J., Ianari, A., McMillan, B., Sellers, W.R.(2021) Mol Cell 81: 3481
- PubMed: 34358446
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V0N, 6V0O - PubMed Abstract:
PRMT5 is an essential arginine methyltransferase and a therapeutic target in MTAP-null cancers. PRMT5 uses adaptor proteins for substrate recruitment through a previously undefined mechanism. Here, we identify an evolutionarily conserved peptide sequence shared among the three known substrate adaptors (CLNS1A, RIOK1, and COPR5) and show that it is necessary and sufficient for interaction with PRMT5. We demonstrate that PRMT5 uses modular adaptor proteins containing a common binding motif for substrate recruitment, comparable with other enzyme classes such as kinases and E3 ligases. We structurally resolve the interface with PRMT5 and show via genetic perturbation that it is required for methylation of adaptor-recruited substrates including the spliceosome, histones, and ribosomal complexes. Furthermore, disruption of this site affects Sm spliceosome activity, leading to intron retention. Genetic disruption of the PRMT5-substrate adaptor interface impairs growth of MTAP-null tumor cells and is thus a site for development of therapeutic inhibitors of PRMT5.
- Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: