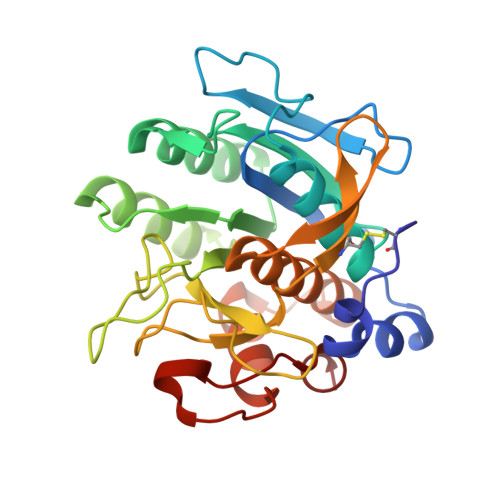
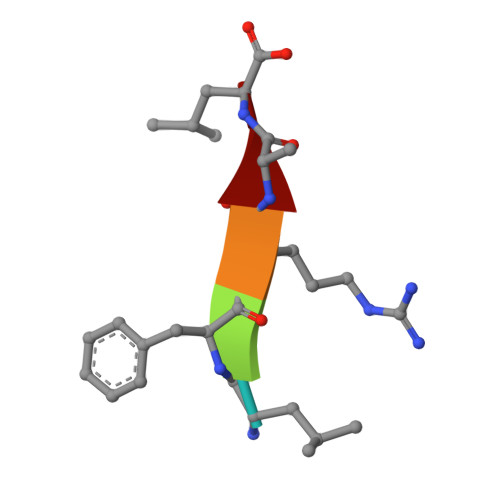
Engineering subtilisin proteases that specifically degrade active RAS.
Chen, Y., Toth, E.A., Ruan, B., Choi, E.J., Simmerman, R., Chen, Y., He, Y., Wang, R., Godoy-Ruiz, R., King, H., Custer, G., Travis Gallagher, D., Rozak, D.A., Solomon, M., Muro, S., Weber, D.J., Orban, J., Fuerst, T.R., Bryan, P.N.(2021) Commun Biol 4: 299-299
- PubMed: 33674772
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-01818-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6U9L, 6UAI, 6UAO, 6UBE - PubMed Abstract:
We describe the design, kinetic properties, and structures of engineered subtilisin proteases that degrade the active form of RAS by cleaving a conserved sequence in switch 2. RAS is a signaling protein that, when mutated, drives a third of human cancers. To generate high specificity for the RAS target sequence, the active site was modified to be dependent on a cofactor (imidazole or nitrite) and protease sub-sites were engineered to create a linkage between substrate and cofactor binding. Selective proteolysis of active RAS arises from a 2-step process wherein sub-site interactions promote productive binding of the cofactor, enabling cleavage. Proteases engineered in this way specifically cleave active RAS in vitro, deplete the level of RAS in a bacterial reporter system, and also degrade RAS in human cell culture. Although these proteases target active RAS, the underlying design principles are fundamental and will be adaptable to many target proteins.
- Potomac Affinity Proteins, North Potomac, MD, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: