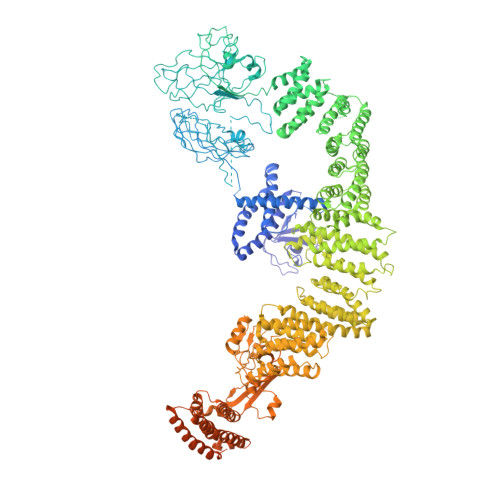
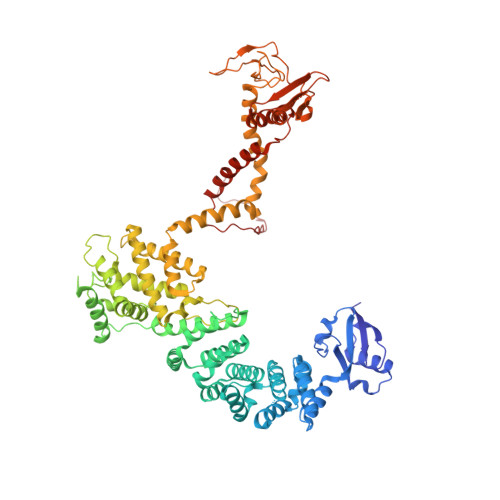
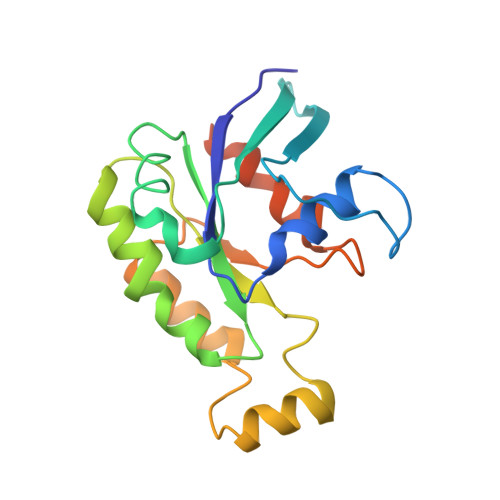
Structure of the DOCK2-ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state.
Chang, L., Yang, J., Jo, C.H., Boland, A., Zhang, Z., McLaughlin, S.H., Abu-Thuraia, A., Killoran, R.C., Smith, M.J., Cote, J.F., Barford, D.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 3464-3464
- PubMed: 32651375
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17271-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TGB, 6TGC, 6UKA - PubMed Abstract:
DOCK (dedicator of cytokinesis) proteins are multidomain guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for RHO GTPases that regulate intracellular actin dynamics. DOCK proteins share catalytic (DOCK DHR2 ) and membrane-associated (DOCK DHR1 ) domains. The structurally-related DOCK1 and DOCK2 GEFs are specific for RAC, and require ELMO (engulfment and cell motility) proteins for function. The N-terminal RAS-binding domain (RBD) of ELMO (ELMO RBD ) interacts with RHOG to modulate DOCK1/2 activity. Here, we determine the cryo-EM structures of DOCK2-ELMO1 alone, and as a ternary complex with RAC1, together with the crystal structure of a RHOG-ELMO2 RBD complex. The binary DOCK2-ELMO1 complex adopts a closed, auto-inhibited conformation. Relief of auto-inhibition to an active, open state, due to a conformational change of the ELMO1 subunit, exposes binding sites for RAC1 on DOCK2 DHR2 , and RHOG and BAI GPCRs on ELMO1. Our structure explains how up-stream effectors, including DOCK2 and ELMO1 phosphorylation, destabilise the auto-inhibited state to promote an active GEF.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, CB2 0QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: