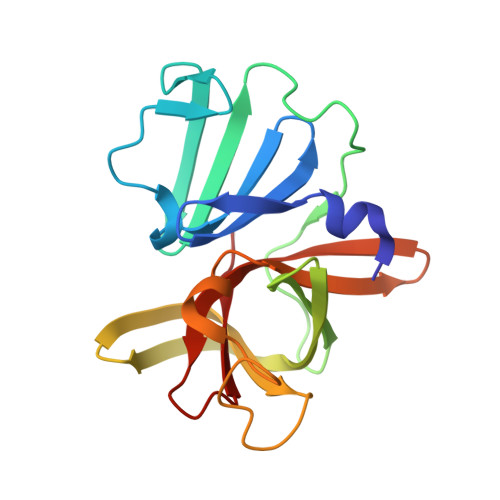
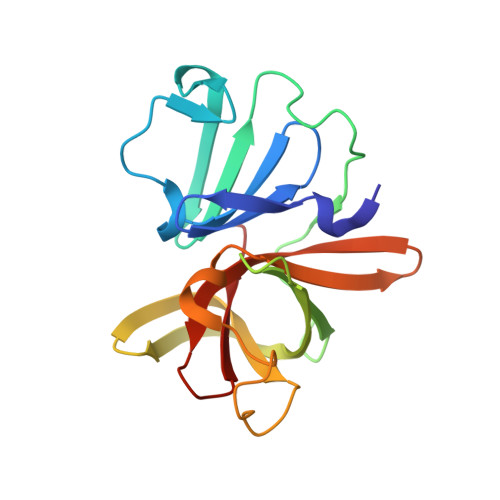
In crystallo-screening for discovery of human norovirus 3C-like protease inhibitors.
Guo, J., Douangamath, A., Song, W., Coker, A.R., Chan, A.W.E., Wood, S.P., Cooper, J.B., Resnick, E., London, N., Delft, F.V.(2020) J Struct Biol X 4: 100031-100031
- PubMed: 32743543
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjsbx.2020.100031
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6T1Q, 6T2I, 6T2X, 6T3G, 6T49, 6T4E, 6T4S, 6T5D, 6T5R, 6T6W, 6T71, 6T82, 6T8R, 6T8T, 6TAL, 6TAW, 6TBO, 6TBP, 6TC1, 6TCF, 6TGL - PubMed Abstract:
Outbreaks of human epidemic nonbacterial gastroenteritis are mainly caused by noroviruses. Viral replication requires a 3C-like cysteine protease (3CL pro ) which processes the 200 kDa viral polyprotein into six functional proteins. The 3CL pro has attracted much interest due to its potential as a target for antiviral drugs. A system for growing high-quality crystals of native Southampton norovirus 3CL pro (SV3CP) has been established, allowing the ligand-free crystal structure to be determined to 1.3 Å in a tetrameric state. This also allowed crystal-based fragment screening to be performed with various compound libraries, ultimately to guide drug discovery for SV3CP. A total of 19 fragments were found to bind to the protease out of the 844 which were screened. Two of the hits were located at the active site of SV3CP and showed good inhibitory activity in kinetic assays. Another 5 were found at the enzyme's putative RNA-binding site and a further 11 were located in the symmetric central cavity of the tetramer.
- Division of Medicine, UCL, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: