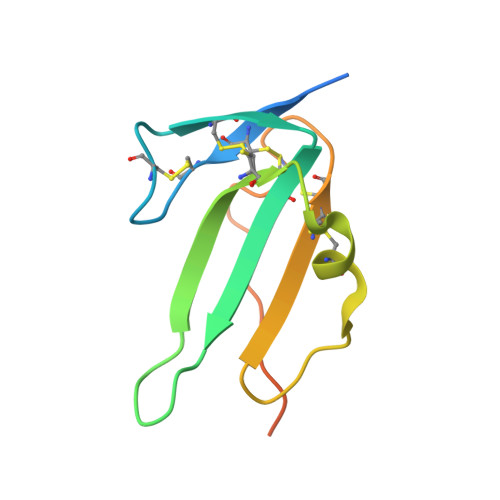
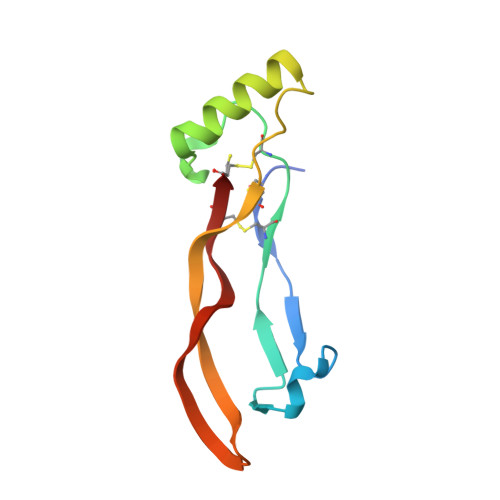
Molecular basis of ALK1-mediated signalling by BMP9/BMP10 and their prodomain-bound forms.
Salmon, R.M., Guo, J., Wood, J.H., Tong, Z., Beech, J.S., Lawera, A., Yu, M., Grainger, D.J., Reckless, J., Morrell, N.W., Li, W.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 1621-1621
- PubMed: 32238803
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15425-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6SF1, 6SF2, 6SF3 - PubMed Abstract:
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1)-mediated endothelial cell signalling in response to bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) and BMP10 is of significant importance in cardiovascular disease and cancer. However, detailed molecular mechanisms of ALK1-mediated signalling remain unclear. Here, we report crystal structures of the BMP10:ALK1 complex at 2.3 Å and the prodomain-bound BMP9:ALK1 complex at 3.3 Å. Structural analyses reveal a tripartite recognition mechanism that defines BMP9 and BMP10 specificity for ALK1, and predict that crossveinless 2 is not an inhibitor of BMP9, which is confirmed by experimental evidence. Introduction of BMP10-specific residues into BMP9 yields BMP10-like ligands with diminished signalling activity in C2C12 cells, validating the tripartite mechanism. The loss of osteogenic signalling in C2C12 does not translate into non-osteogenic activity in vivo and BMP10 also induces bone-formation. Collectively, these data provide insight into ALK1-mediated BMP9 and BMP10 signalling, facilitating therapeutic targeting of this important pathway.
- The Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine, Cambridge, CB2 0QQ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: