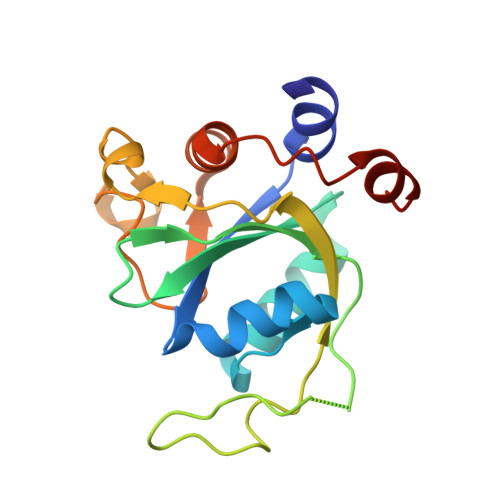
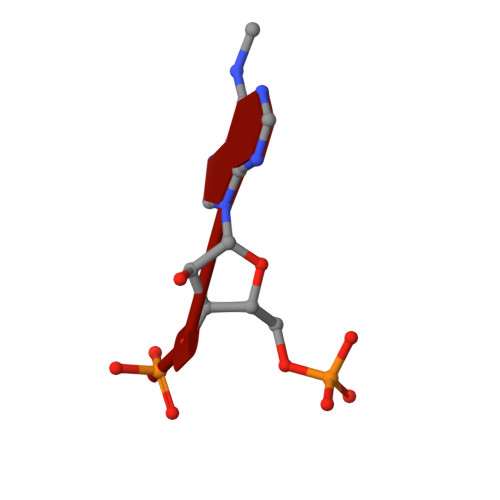
Flexible Binding of m6A Reader Protein YTHDC1 to Its Preferred RNA Motif.
Li, Y., Bedi, R.K., Wiedmer, L., Huang, D., Sledz, P., Caflisch, A.(2019) J Chem Theory Comput 15: 7004-7014
- PubMed: 31670957
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.9b00987
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RT4, 6RT5, 6RT6, 6RT7 - PubMed Abstract:
N 6 -Methyladenosine (m 6 A) is the most prevalent chemical modification in human mRNAs. Its recognition by reader proteins enables many cellular functions, including splicing and translation of mRNAs. However, the binding mechanisms of m 6 A-containing RNAs to their readers are still elusive due to the unclear roles of m 6 A-flanking ribonucleotides. Here, we use a model system, YTHDC1 with its RNA motif 5'-G -2 G -1 (m 6 A)C +1 U +2 -3', to investigate the binding mechanisms by atomistic simulations, X-ray crystallography, and isothermal titration calorimetry. The experimental data and simulation results show that m 6 A is captured by an aromatic cage of YTHDC1 and the 3' terminus nucleotides are stabilized by cation-π-π interactions, while the 5' terminus remains flexible. Notably, simulations of unbound RNA motifs reveal that the methyl group of m 6 A and the 5' terminus shift the conformational preferences of the oligoribonucleotide to the bound-like conformation, thereby facilitating the association process. The binding mechanisms may help in the discovery of chemical probes against m 6 A reader proteins.
- Department of Biochemistry , University of Zurich , Winterthurerstrasse 190 , CH-8057 Zurich , Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: