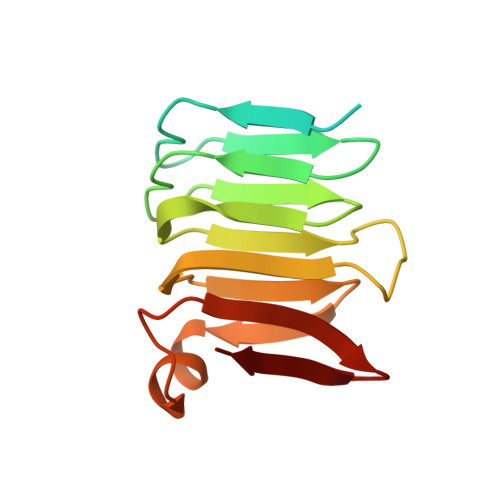
Cryo-EM structure of the MinCD copolymeric filament from Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.1 angstrom resolution.
Szewczak-Harris, A., Wagstaff, J., Lowe, J.(2019) FEBS Lett 593: 1915-1926
- PubMed: 31166018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13471
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RIQ - PubMed Abstract:
Positioning of the division site in many bacterial species relies on the MinCDE system, which prevents the cytokinetic Z-ring from assembling anywhere but the mid-cell, through an oscillatory diffusion-reaction mechanism. MinD dimers bind to membranes and, via their partner MinC, inhibit the polymerization of cell division protein FtsZ into the Z-ring. MinC and MinD form polymeric assemblies in solution and on cell membranes. Here, we report the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of the copolymeric filaments of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MinCD. The filaments consist of three protofilaments made of alternating MinC and MinD dimers. The MinCD protofilaments are almost completely straight and assemble as single protofilaments on lipid membranes, which we also visualized by cryo-EM.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: