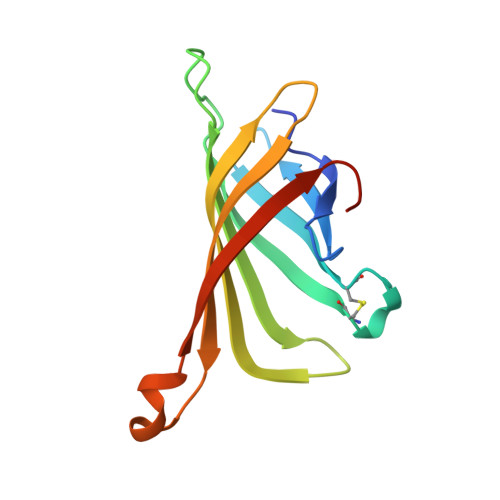
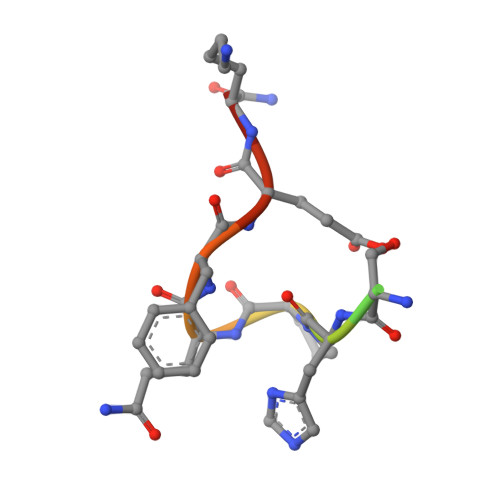
The Role of Changing Loop Conformations in Streptavidin Versions Engineered for High-affinity Binding of the Strep-tag II Peptide.
Schmidt, T.G.M., Eichinger, A., Schneider, M., Bonet, L., Carl, U., Karthaus, D., Theobald, I., Skerra, A.(2021) J Mol Biology 433: 166893-166893
- PubMed: 33639211
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166893
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6QBB, 6QSY, 6QW4, 6SOK, 6SOS, 6TIP - PubMed Abstract:
The affinity system based on the artificial peptide ligand Strep-tag® II and engineered tetrameric streptavidin, known as Strep-Tactin®, offers attractive applications for the study of recombinant proteins, from detection and purification to functional immobilization. To further improve binding of the Strep-tag II to streptavidin we have subjected two protruding loops that shape its ligand pocket for the peptide - instead of D-biotin recognized by the natural protein - to iterative random mutagenesis. Sequence analyses of hits from functional screening assays revealed several unexpected structural motifs, such as a disulfide bridge at the base of one loop, replacement of the crucial residue Trp120 by Gly and a two-residue deletion in the second loop. The mutant m1-9 (dubbed Strep-Tactin XT) showed strongly enhanced affinity towards the Strep-tag II, which was further boosted in case of the bivalent Twin-Strep-tag®. Four representative streptavidin mutants were crystallized in complex with the Strep-tag II peptide and their X-ray structures were solved at high resolutions. In addition, the crystal structure of the complex between Strep-Tactin XT and the Twin-Strep-tag was elucidated, indicating a bivalent mode of binding and explaining the experimentally observed avidity effect. Our study illustrates the structural plasticity of streptavidin as a scaffold for ligand binding and reveals interaction modes that would have been difficult to predict. As result, Strep-Tactin XT offers a convenient reagent for the kinetically stable immobilization of recombinant proteins fused with the Twin-Strep-tag. The possibility of reversibly dissociating such complexes simply with D-biotin as a competing ligand enables functional studies in protein science as well as cell biology.
- IBA GmbH, Rudolf-Wissell-Str. 28, 37079 Göttingen, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: