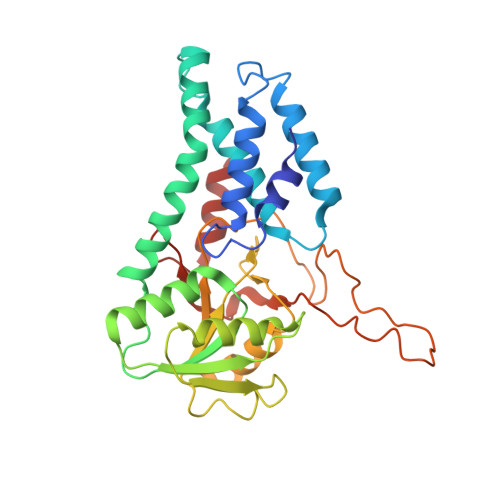
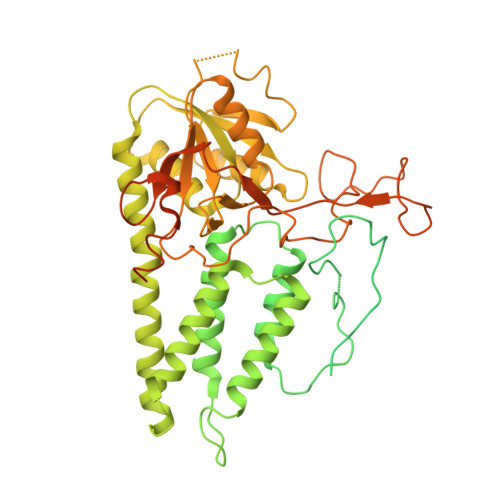
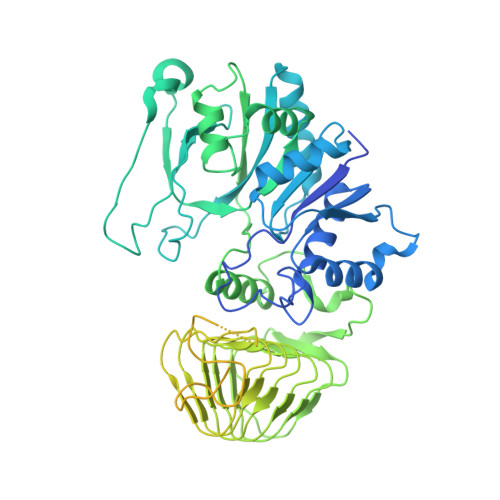
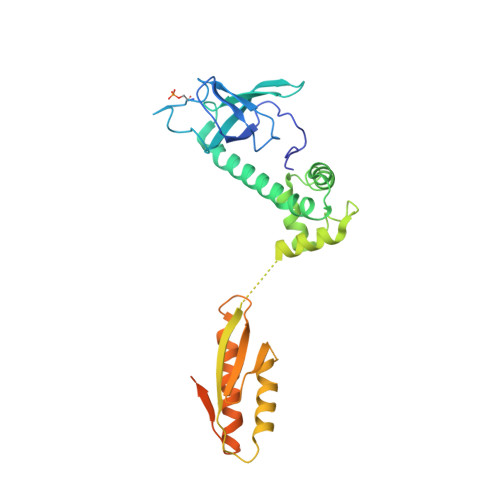
Structural basis for the inhibition of translation through eIF2 alpha phosphorylation.
Gordiyenko, Y., Llacer, J.L., Ramakrishnan, V.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 2640-2640
- PubMed: 31201334
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10606-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6QG0, 6QG1, 6QG2, 6QG3, 6QG5, 6QG6 - PubMed Abstract:
One of the responses to stress by eukaryotic cells is the down-regulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF2. Phosphorylation results in low availability of the eIF2 ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-tRNAi) by affecting the interaction of eIF2 with its GTP-GDP exchange factor eIF2B. We have determined the cryo-EM structure of yeast eIF2B in complex with phosphorylated eIF2 at an overall resolution of 4.2 Å. Two eIF2 molecules bind opposite sides of an eIF2B hetero-decamer through eIF2α-D1, which contains the phosphorylated Ser51. eIF2α-D1 is mainly inserted between the N-terminal helix bundle domains of δ and α subunits of eIF2B. Phosphorylation of Ser51 enhances binding to eIF2B through direct interactions of phosphate groups with residues in eIF2Bα and indirectly by inducing contacts of eIF2α helix 58-63 with eIF2Bδ leading to a competition with Met-tRNA i .
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge, CB2 0QH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: