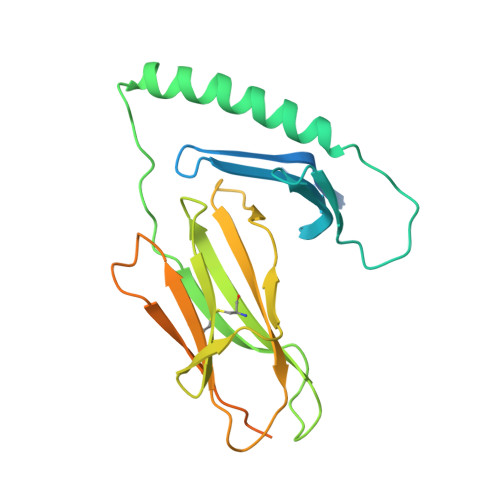
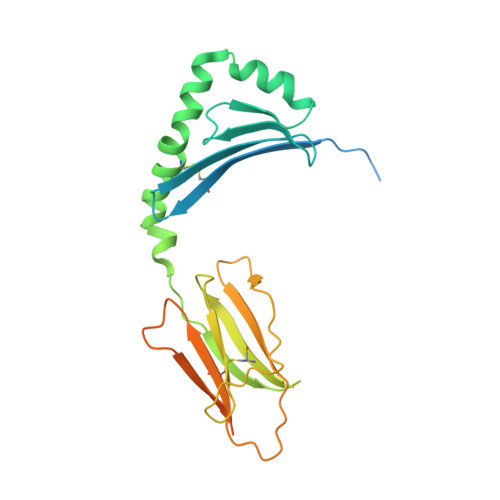
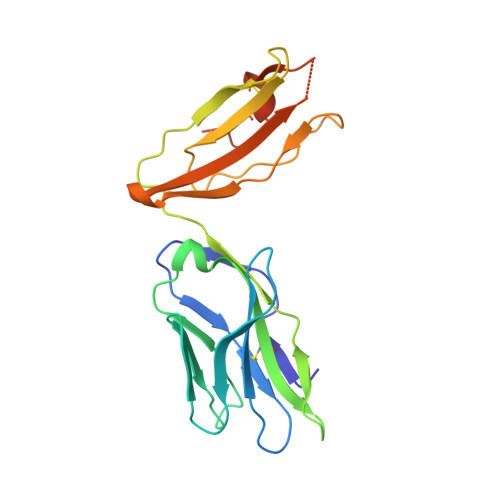
A molecular basis for the T cell response in HLA-DQ2.2 mediated celiac disease.
Ting, Y.T., Dahal-Koirala, S., Kim, H.S.K., Qiao, S.W., Neumann, R.S., Lundin, K.E.A., Petersen, J., Reid, H.H., Sollid, L.M., Rossjohn, J.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 3063-3073
- PubMed: 31974305
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1914308117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PX6, 6PY2 - PubMed Abstract:
The highly homologous human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ2 molecules, HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ2.2, are implicated in the pathogenesis of celiac disease (CeD) by presenting gluten peptides to CD4 + T cells. However, while HLA-DQ2.5 is strongly associated with disease, HLA-DQ2.2 is not, and the molecular basis underpinning this differential disease association is unresolved. We here provide structural evidence for how the single polymorphic residue (HLA-DQ2.5-Tyr22α and HLA-DQ2.2-Phe22α) accounts for HLA-DQ2.2 additionally requiring gluten epitopes possessing a serine at the P3 position of the peptide. In marked contrast to the biased T cell receptor (TCR) usage associated with HLA-DQ2.5-mediated CeD, we demonstrate with extensive single-cell sequencing that a diverse TCR repertoire enables recognition of the immunodominant HLA-DQ2.2-glut-L1 epitope. The crystal structure of two CeD patient-derived TCR in complex with HLA-DQ2.2 and DQ2.2-glut-L1 (PFSEQEQPV) revealed a docking strategy, and associated interatomic contacts, which was notably distinct from the structures of the TCR:HLA-DQ2.5:gliadin epitope complexes. Accordingly, while the molecular surfaces of the antigen-binding clefts of HLA-DQ2.5 and HLA-DQ2.2 are very similar, differences in the nature of the peptides presented translates to differences in responding T cell repertoires and the nature of engagement of the respective antigen-presenting molecules, which ultimately is associated with differing disease penetrance.
- Infection and Immunity Program, Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University, Clayton, VIC 3800, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: