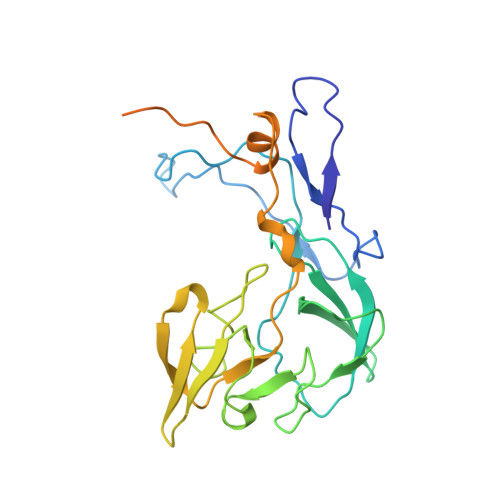
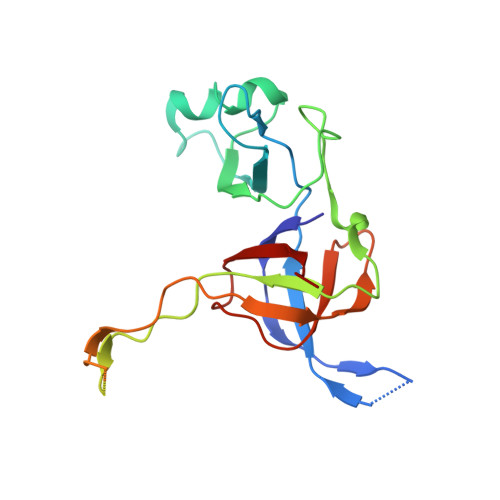
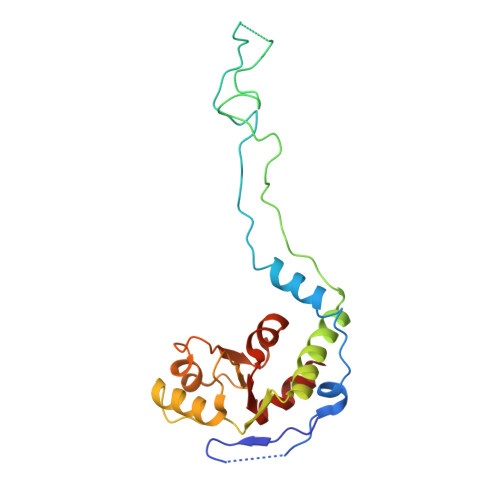
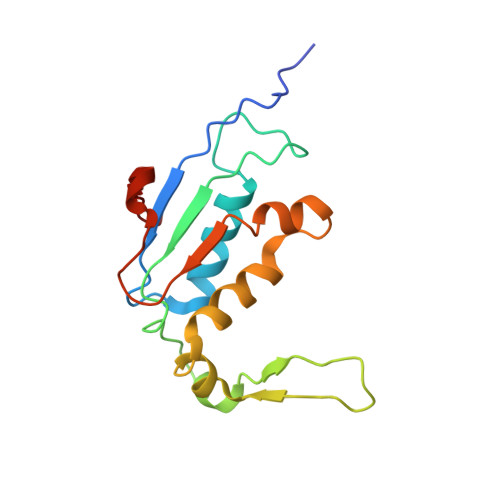
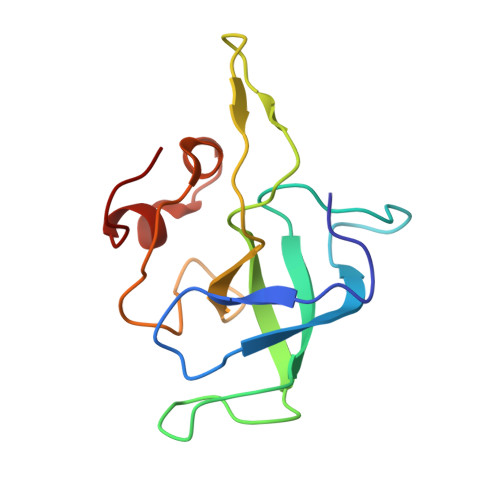
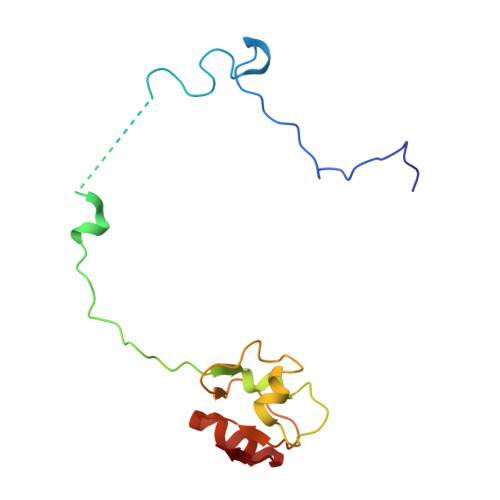
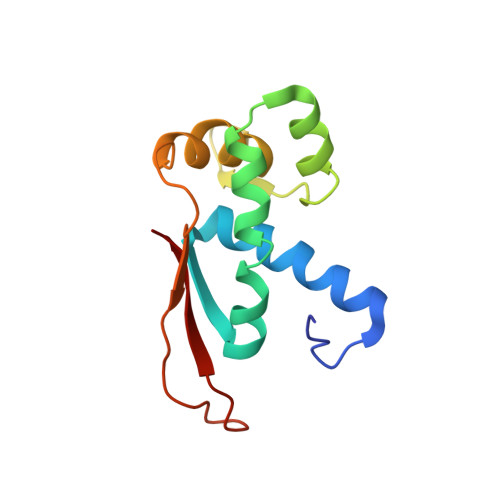
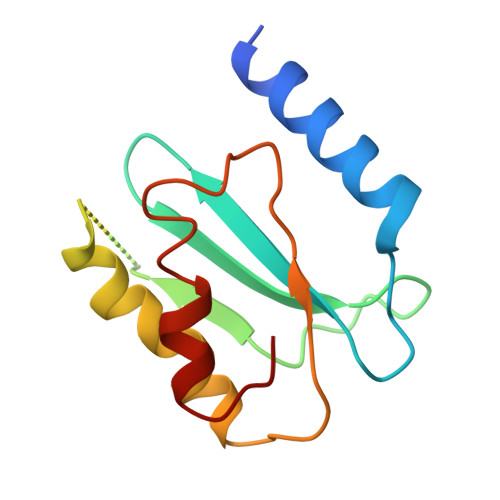
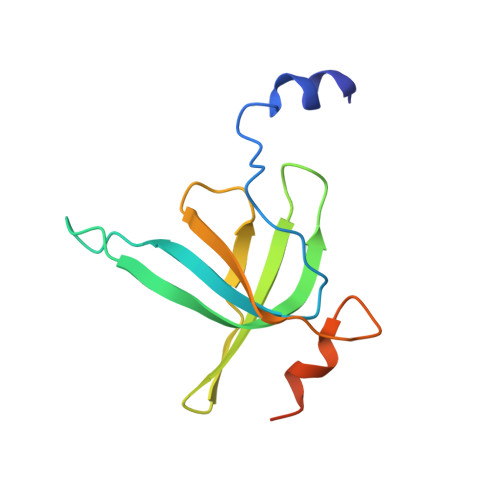
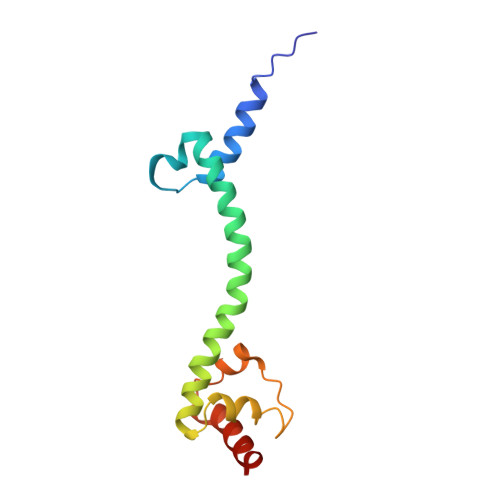
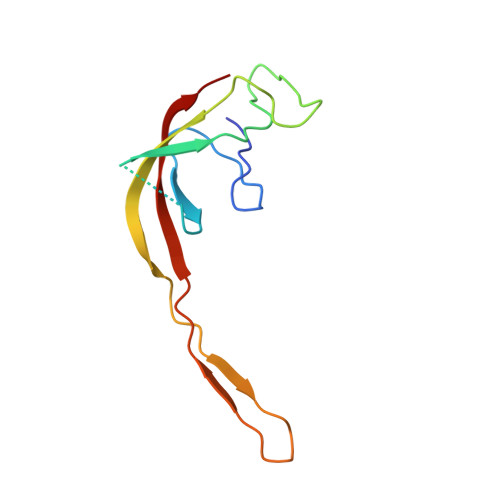
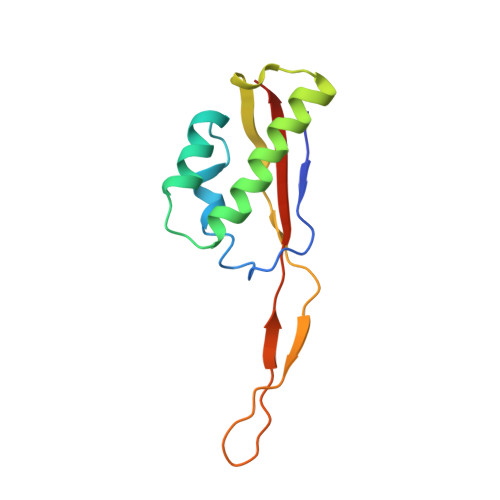
Structural consequences of the interaction of RbgA with a 50S ribosomal subunit assembly intermediate.
Seffouh, A., Jain, N., Jahagirdar, D., Basu, K., Razi, A., Ni, X., Guarne, A., Britton, R.A., Ortega, J.(2019) Nucleic Acids Res 47: 10414-10425
- PubMed: 31665744
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz770
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PPF, 6PPK, 6PVK - PubMed Abstract:
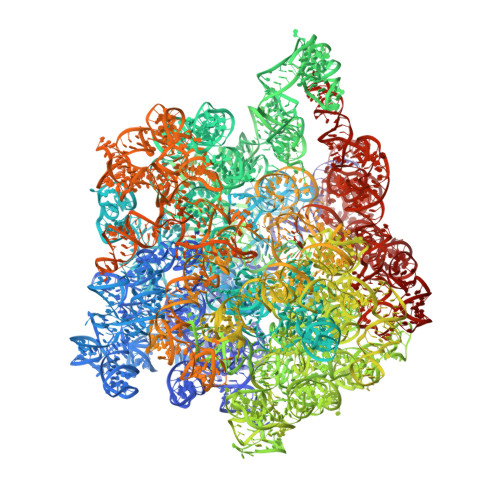
Bacteria harbor a number GTPases that function in the assembly of the ribosome and are essential for growth. RbgA is one of these GTPases and is required for the assembly of the 50S subunit in most bacteria. Homologs of this protein are also implicated in the assembly of the large subunit of the mitochondrial and eukaryotic ribosome. We present here the cryo-electron microscopy structure of RbgA bound to a Bacillus subtilis 50S subunit assembly intermediate (45SRbgA particle) that accumulates in cells upon RbgA depletion. Binding of RbgA at the P site of the immature particle stabilizes functionally important rRNA helices in the A and P-sites, prior to the completion of the maturation process of the subunit. The structure also reveals the location of the highly conserved N-terminal end of RbgA containing the catalytic residue Histidine 9. The derived model supports a mechanism of GTP hydrolysis, and it shows that upon interaction of RbgA with the 45SRbgA particle, Histidine 9 positions itself near the nucleotide potentially acting as the catalytic residue with minimal rearrangements. This structure represents the first visualization of the conformational changes induced by an assembly factor in a bacterial subunit intermediate.
- Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec H3A 0C7, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: