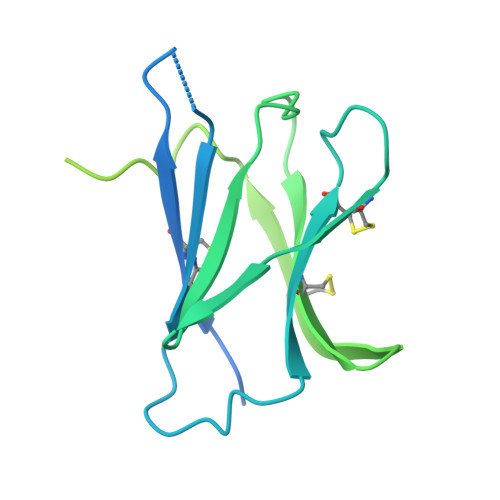
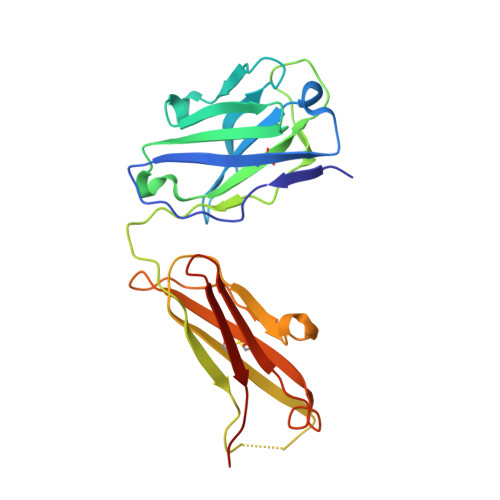
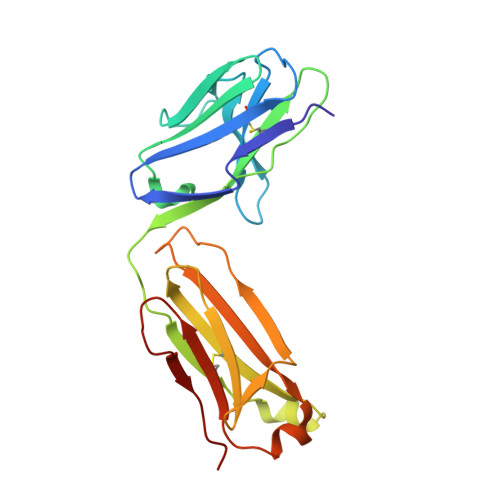
New anti-IL-7R alpha monoclonal antibodies show efficacy against T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in pre-clinical models.
Hixon, J.A., Andrews, C., Kashi, L., Kohnhorst, C.L., Senkevitch, E., Czarra, K., Barata, J.T., Li, W., Schneider, J.P., Walsh, S.T.R., Durum, S.K.(2020) Leukemia 34: 35-49
- PubMed: 31439943
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0531-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6P4Y, 6P50, 6P67 - PubMed Abstract:
Pediatric T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells frequently contain mutations in the interleukin-7 (IL-7) receptor pathway or respond to IL-7 itself. To target the IL-7 receptor on T-ALL cells, murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) were developed against the human IL-7Rα chain and chimerized with human IgG1 constant regions. Crystal structures demonstrate that the two MAbs bound different IL-7Rα epitopes. The MAbs mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against patient-derived xenograft (PDX) T-ALL cells, which was improved by combining two MAbs. In vivo, the MAbs showed therapeutic efficacy via ADCC-dependent and independent mechanisms in minimal residual and established disease. PDX T-ALL cells that relapsed following a course of chemotherapy displayed elevated IL-7Rα, and MAb treatment is effective against relapsing disease, suggesting the use of anti-IL7Rα MAbs in relapsed T-ALL patients or patients that do not respond to chemotherapy.
- Cytokines and Immunity Section, Cancer and Inflammation Program (CIP), National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Frederick, MD, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: