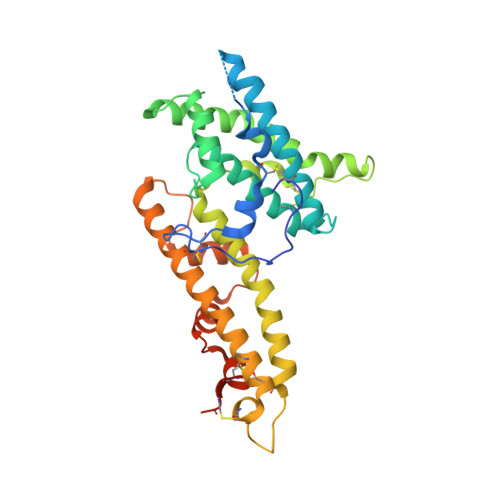
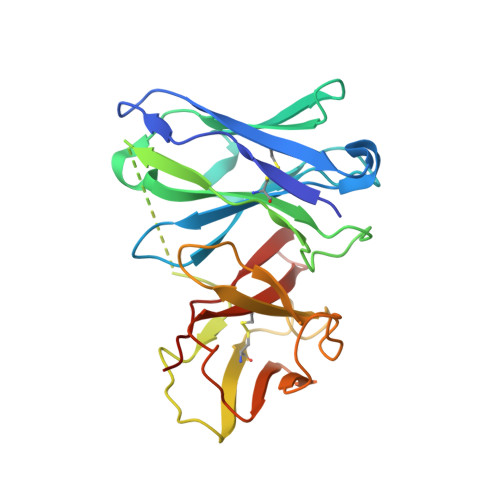
Structural basis for neutralization of Plasmodium vivax by naturally acquired human antibodies that target DBP.
Urusova, D., Carias, L., Huang, Y., Nicolete, V.C., Popovici, J., Roesch, C., Salinas, N.D., Witkowski, B., Ferreira, M.U., Adams, J.H., Gross, M.L., King, C.L., Tolia, N.H.(2019) Nat Microbiol 4: 1486-1496
- PubMed: 31133752
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0461-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OAN, 6OAO - PubMed Abstract:
The Plasmodium vivax Duffy-binding protein (DBP) is a prime target of the protective immune response and a promising vaccine candidate for P. vivax malaria. Naturally acquired immunity (NAI) protects against malaria in adults residing in infection-endemic regions, and the passive transfer of malarial immunity confers protection. A vaccine that replicates NAI will effectively prevent disease. Here, we report the structures of DBP region II in complex with human-derived, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies obtained from an individual in a malaria-endemic area with NAI. We identified protective epitopes using X-ray crystallography, hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, mutational mapping and P. vivax invasion studies. These approaches reveal that naturally acquired human antibodies neutralize P. vivax by targeting the binding site for Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC) and the dimer interface of P. vivax DBP. Antibody binding is unaffected by polymorphisms in the vicinity of epitopes, suggesting that the antibodies have evolved to engage multiple polymorphic variants of DBP. The human antibody epitopes are broadly conserved and are distinct from previously defined epitopes for broadly conserved murine monoclonal antibodies. A library of globally conserved epitopes of neutralizing human antibodies offers possibilities for rational design of strain-transcending DBP-based vaccines and therapeutics against P. vivax.
- Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, MO, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: