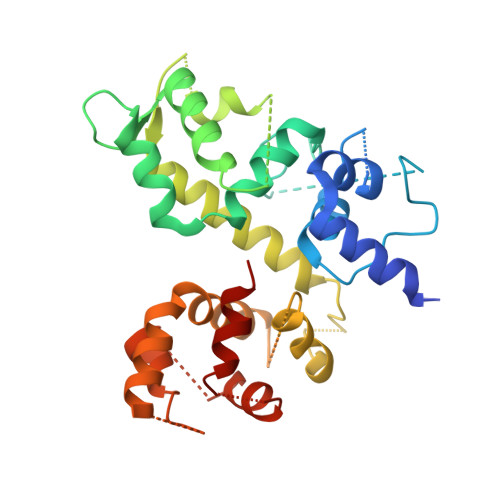
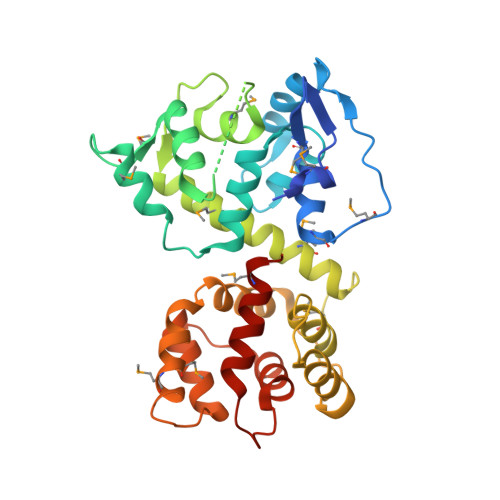
Structure of the MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer provides insights into the gatekeeping threshold shift.
Park, J., Lee, Y., Park, T., Kang, J.Y., Mun, S.A., Jin, M., Yang, J., Eom, S.H.(2020) IUCrJ 7: 355-365
- PubMed: 32148862
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252520001840
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LE5 - PubMed Abstract:
Mitochondrial calcium uptake proteins 1 and 2 (MICU1 and MICU2) mediate mitochondrial Ca 2+ influx via the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU). Its molecular action for Ca 2+ uptake is tightly controlled by the MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer, which comprises Ca 2+ sensing proteins which act as gatekeepers at low [Ca 2+ ] or facilitators at high [Ca 2+ ]. However, the mechanism underlying the regulation of the Ca 2+ gatekeeping threshold for mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake through the MCU by the MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer remains unclear. In this study, we determined the crystal structure of the apo form of the human MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer that functions as the MCU gatekeeper. MICU1 and MICU2 assemble in the face-to-face heterodimer with salt bridges and me-thio-nine knobs stabilizing the heterodimer in an apo state. Structural analysis suggests how the heterodimer sets a higher Ca 2+ threshold than the MICU1 homodimer. The structure of the heterodimer in the apo state provides a framework for understanding the gatekeeping role of the MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer.
- School of Life Sciences, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Buk-gu, Gwangju 61005, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: