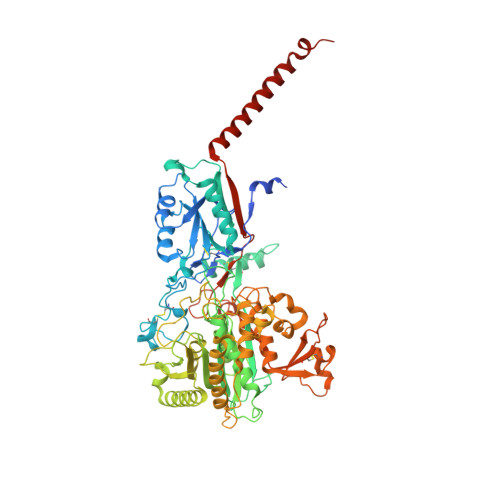
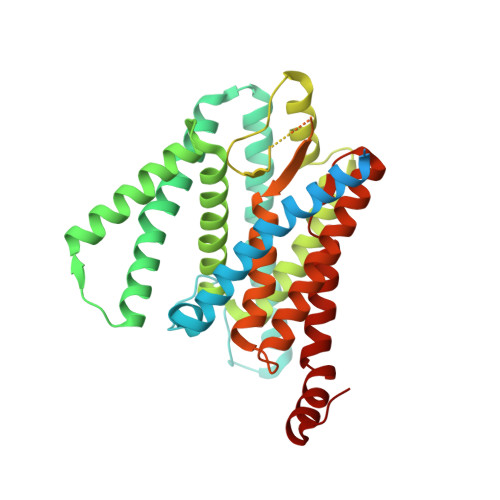
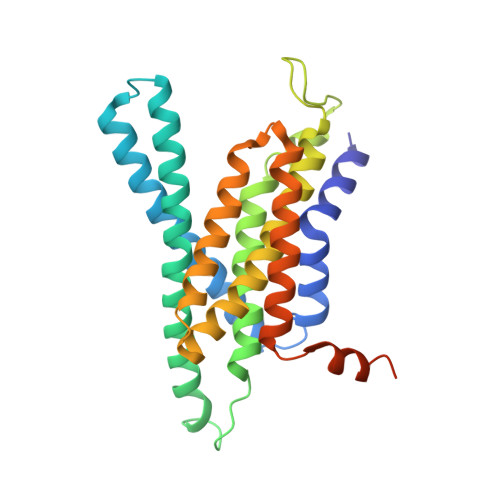
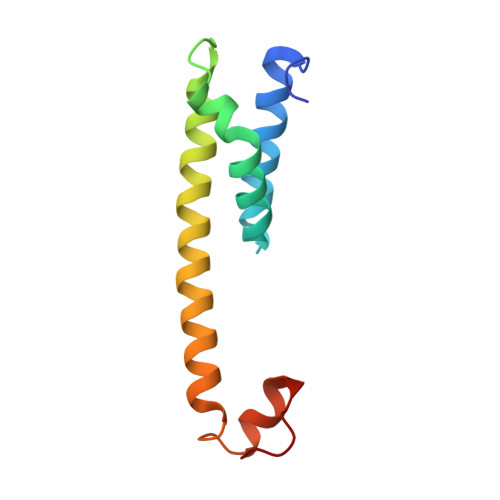
Recognition of the amyloid precursor protein by human gamma-secretase.
Zhou, R., Yang, G., Guo, X., Zhou, Q., Lei, J., Shi, Y.(2019) Science 363
- PubMed: 30630874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw0930
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IYC - PubMed Abstract:
Cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by the intramembrane protease γ-secretase is linked to Alzheimer's disease (AD). We report an atomic structure of human γ-secretase in complex with a transmembrane (TM) APP fragment at 2.6-angstrom resolution. The TM helix of APP closely interacts with five surrounding TMs of PS1 (the catalytic subunit of γ-secretase). A hybrid β sheet, which is formed by a β strand from APP and two β strands from PS1, guides γ-secretase to the scissile peptide bond of APP between its TM and β strand. Residues at the interface between PS1 and APP are heavily targeted by recurring mutations from AD patients. This structure, together with that of γ-secretase bound to Notch, reveal contrasting features of substrate binding, which may be applied toward the design of substrate-specific inhibitors.
- Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
Organizational Affiliation: