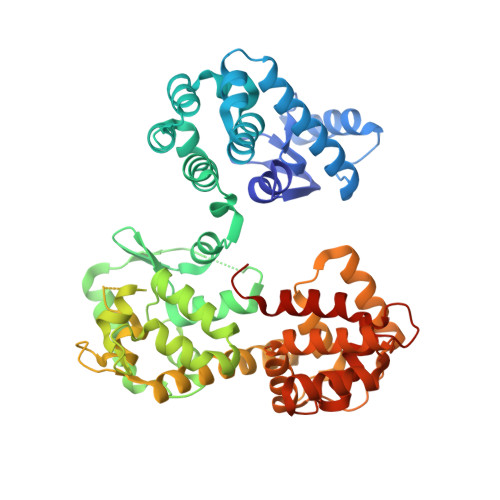
The crystal structure of MICU2 provides insight into Ca2+binding and MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer formation.
Wu, W., Shen, Q., Lei, Z., Qiu, Z., Li, D., Pei, H., Zheng, J., Jia, Z.(2019) EMBO Rep 20: e47488-e47488
- PubMed: 31397067
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201847488
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IIH - PubMed Abstract:
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex mediates the uptake of Ca 2+ into mitochondria. Its activity is regulated by a heterodimer of MICU1 and MICU2, two EF-hand-containing proteins that act as the main gatekeeper of the uniporter. Herein we report the crystal structure of human MICU2 at 1.96 Å resolution. Our structure reveals a dimeric architecture of MICU2, in which each monomer adopts the canonical two-lobe structure with a pair of EF-hands in each lobe. Both Ca 2+ -bound and Ca 2+ -free EF-hands are observed in our structure. Moreover, we characterize the interaction sites within the MICU2 homodimer, as well as the MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer in both Ca 2+ -free and Ca 2+ -bound conditions. Glu242 in MICU1 and Arg352 in MICU2 are crucial for apo heterodimer formation, while Phe383 in MICU1 and Glu196 in MICU2 significantly contribute to the interaction in the Ca 2+ -bound state. Based on our structural and biochemical analyses, we propose a model for MICU1-MICU2 heterodimer formation and its conformational transition from apo to a more compact Ca 2+ -bound state, which expands our understanding of this co-regulatory mechanism critical for MCU's mitochondrial calcium uptake function.
- College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China.
Organizational Affiliation: