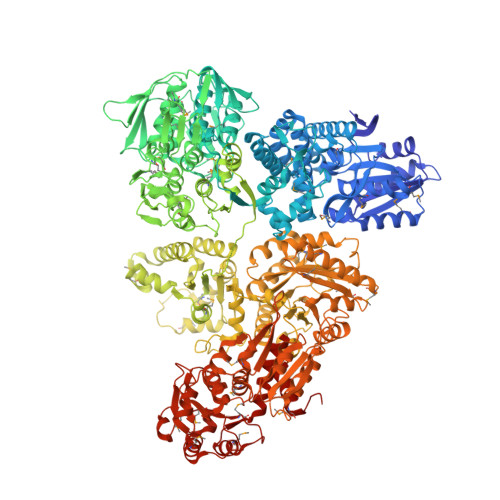
Architecture and functional dynamics of the pentafunctional AROM complex.
Arora Veraszto, H., Logotheti, M., Albrecht, R., Leitner, A., Zhu, H., Hartmann, M.D.(2020) Nat Chem Biol 16: 973-978
- PubMed: 32632294
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0587-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HQV - PubMed Abstract:
The AROM complex is a multifunctional metabolic machine with ten enzymatic domains catalyzing the five central steps of the shikimate pathway in fungi and protists. We determined its crystal structure and catalytic behavior, and elucidated its conformational space using a combination of experimental and computational approaches. We derived this space in an elementary approach, exploiting an abundance of conformational information from its monofunctional homologs in the Protein Data Bank. It demonstrates how AROM is optimized for spatial compactness while allowing for unrestricted conformational transitions and a decoupled functioning of its individual enzymatic entities. With this architecture, AROM poses a tractable test case for the effects of active site proximity on the efficiency of both natural metabolic systems and biotechnological pathway optimization approaches. We show that a mere colocalization of enzymes is not sufficient to yield a detectable improvement of metabolic throughput.
- Department of Protein Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Tübingen, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: