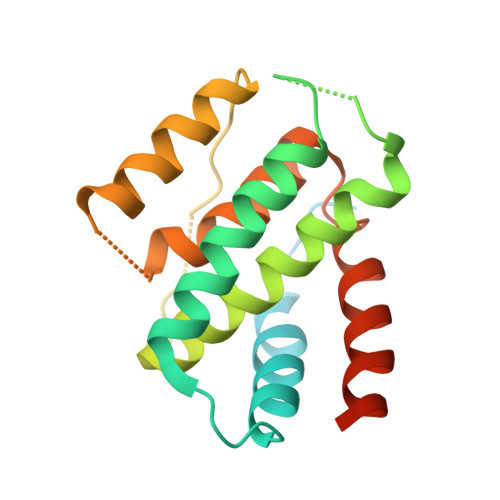
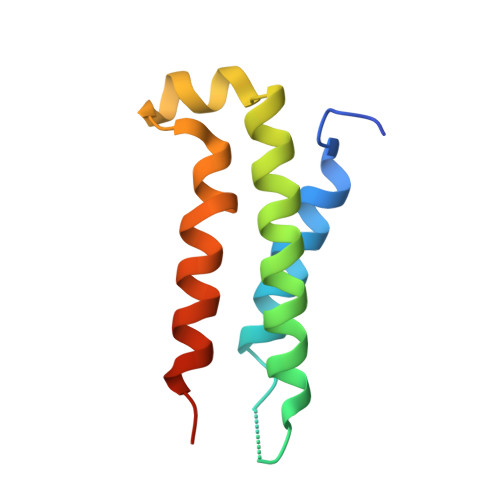
The structure of a polygamous repressor reveals how phage-inducible chromosomal islands spread in nature.
Rafael Ciges-Tomas, J., Alite, C., Humphrey, S., Donderis, J., Bowring, J., Salvatella, X., Penades, J.R., Marina, A.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 3676-3676
- PubMed: 31417084
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11504-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H48, 6H49, 6H4B, 6H4C - PubMed Abstract:
Stl is a master repressor encoded by Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity islands (SaPIs) that maintains integration of these elements in the bacterial chromosome. After infection or induction of a resident helper phage, SaPIs are de-repressed by specific interactions of phage proteins with Stl. SaPIs have evolved a fascinating mechanism to ensure their promiscuous transfer by targeting structurally unrelated proteins performing identically conserved functions for the phage. Here we decipher the molecular mechanism of this elegant strategy by determining the structure of SaPIbov1 Stl alone and in complex with two structurally unrelated dUTPases from different S. aureus phages. Remarkably, SaPIbov1 Stl has evolved different domains implicated in DNA and partner recognition specificity. This work presents the solved structure of a SaPI repressor protein and the discovery of a modular repressor that acquires multispecificity through domain recruiting. Our results establish the mechanism that allows widespread dissemination of SaPIs in nature.
- Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia (IBV-CSIC) and CIBER de Enfermedades Raras (CIBERER), Valencia, 46010, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: