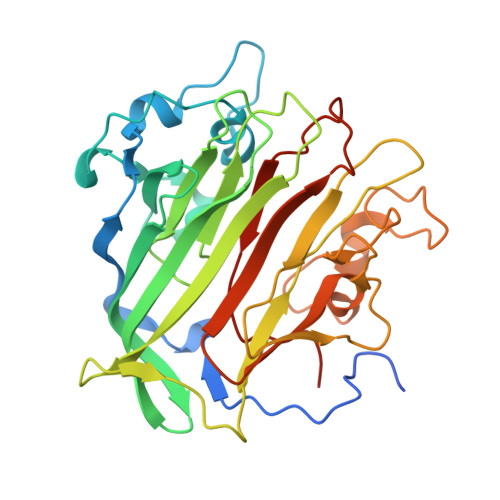
PrgB promotes aggregation, biofilm formation, and conjugation through DNA binding and compaction.
Schmitt, A., Jiang, K., Camacho, M.I., Jonna, V.R., Hofer, A., Westerlund, F., Christie, P.J., Berntsson, R.P.(2018) Mol Microbiol 109: 291-305
- PubMed: 29723434
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13980
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EVU, 6GED - PubMed Abstract:
Gram-positive bacteria deploy type IV secretion systems (T4SSs) to facilitate horizontal gene transfer. The T4SSs of Gram-positive bacteria rely on surface adhesins as opposed to conjugative pili to facilitate mating. Enterococcus faecalis PrgB is a surface adhesin that promotes mating pair formation and robust biofilm development in an extracellular DNA (eDNA) dependent manner. Here, we report the structure of the adhesin domain of PrgB. The adhesin domain binds and compacts DNA in vitro. In vivo PrgB deleted of its adhesin domain does not support cellular aggregation, biofilm development and conjugative DNA transfer. PrgB also binds lipoteichoic acid (LTA), which competes with DNA binding. We propose that PrgB binding and compaction of eDNA facilitates cell aggregation and plays an important role in establishment of early biofilms in mono- or polyspecies settings. Within these biofilms, PrgB mediates formation and stabilization of direct cell-cell contacts through alternative binding of cell-bound LTA, which in turn promotes establishment of productive mating junctions and efficient intra- or inter-species T4SS-mediated gene transfer.
- Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Umeå University, SE-90187 Umeå, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: