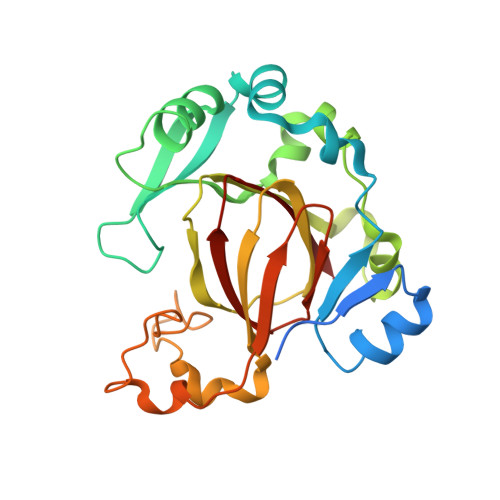
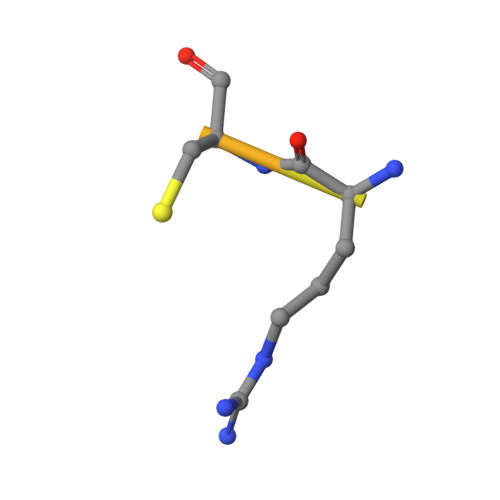
JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase.
Wilkins, S.E., Islam, S., Gannon, J.M., Markolovic, S., Hopkinson, R.J., Ge, W., Schofield, C.J., Chowdhury, R.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 1180-1180
- PubMed: 29563586
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03410-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6F4M, 6F4N, 6F4O, 6F4P, 6F4Q, 6F4R, 6F4S, 6F4T - PubMed Abstract:
Oxygenase-catalysed post-translational modifications of basic protein residues, including lysyl hydroxylations and N ε -methyl lysyl demethylations, have important cellular roles. Jumonji-C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 5 (JMJD5), which genetic studies reveal is essential in animal development, is reported as a histone N ε -methyl lysine demethylase (KDM). Here we report how extensive screening with peptides based on JMJD5 interacting proteins led to the finding that JMJD5 catalyses stereoselective C-3 hydroxylation of arginine residues in sequences from human regulator of chromosome condensation domain-containing protein 1 (RCCD1) and ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6). High-resolution crystallographic analyses reveal overall fold, active site and substrate binding/product release features supporting the assignment of JMJD5 as an arginine hydroxylase rather than a KDM. The results will be useful in the development of selective oxygenase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer and genetic diseases.
- The Department of Chemistry, University of Oxford, Mansfield Road, Oxford, OX1 3TA, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: