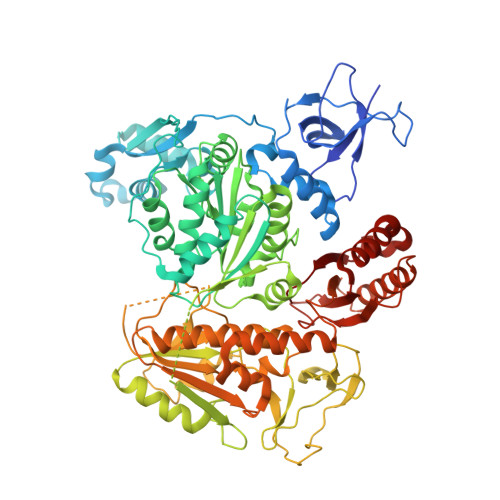
Structure-specific DNA replication-fork recognition directs helicase and replication restart activities of the PriA helicase.
Windgassen, T.A., Leroux, M., Satyshur, K.A., Sandler, S.J., Keck, J.L.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: E9075-E9084
- PubMed: 30201718
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1809842115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DCR, 6DGD - PubMed Abstract:
DNA replication restart, the essential process that reinitiates prematurely terminated genome replication reactions, relies on exquisitely specific recognition of abandoned DNA replication-fork structures. The PriA DNA helicase mediates this process in bacteria through mechanisms that remain poorly defined. We report the crystal structure of a PriA/replication-fork complex, which resolves leading-strand duplex DNA bound to the protein. Interaction with PriA unpairs one end of the DNA and sequesters the 3'-most nucleotide from the nascent leading strand into a conserved protein pocket. Cross-linking studies reveal a surface on the winged-helix domain of PriA that binds to parental duplex DNA. Deleting the winged-helix domain alters PriA's structure-specific DNA unwinding properties and impairs its activity in vivo. Our observations lead to a model in which coordinated parental-, leading-, and lagging-strand DNA binding provide PriA with the structural specificity needed to act on abandoned DNA replication forks.
- Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI 53706.
Organizational Affiliation: