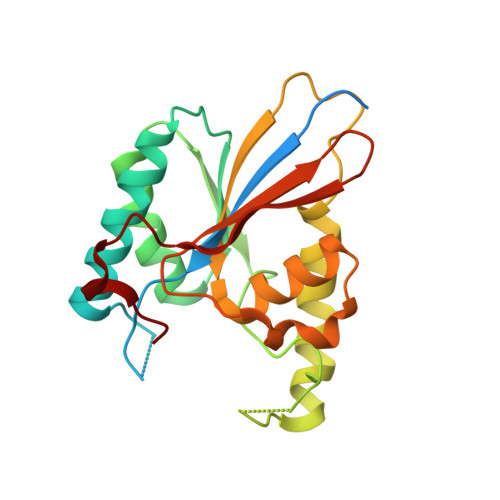
Functional role of PGAM5 multimeric assemblies and their polymerization into filaments.
Ruiz, K., Thaker, T.M., Agnew, C., Miller-Vedam, L., Trenker, R., Herrera, C., Ingaramo, M., Toso, D., Frost, A., Jura, N.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 531-531
- PubMed: 30705304
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08393-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CNI, 6CNL - PubMed Abstract:
PGAM5 is a mitochondrial protein phosphatase whose genetic ablation in mice results in mitochondria-related disorders, including neurodegeneration. Functions of PGAM5 include regulation of mitophagy, cell death, metabolism and aging. However, mechanisms regulating PGAM5 activation and signaling are poorly understood. Using electron cryo-microscopy, we show that PGAM5 forms dodecamers in solution. We also present a crystal structure of PGAM5 that reveals the determinants of dodecamer formation. Furthermore, we observe PGAM5 dodecamer assembly into filaments both in vitro and in cells. We find that PGAM5 oligomerization into a dodecamer is not only essential for catalytic activation, but this form also plays a structural role on mitochondrial membranes, which is independent of phosphatase activity. Together, these findings suggest that modulation of the oligomerization of PGAM5 may be a regulatory switch of potential therapeutic interest.
- Cardiovascular Research Institute, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 94158, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: