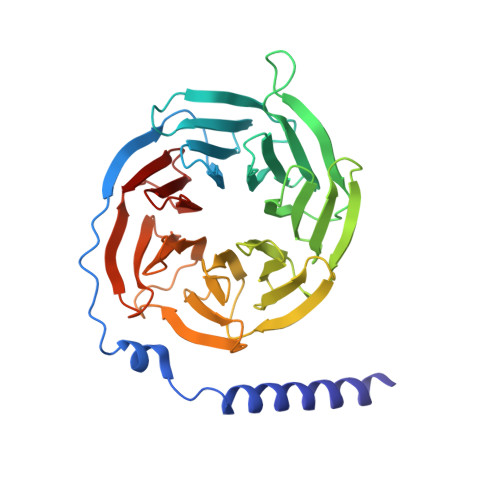
Targeting G protein-coupled receptor signaling at the G protein level with a selective nanobody inhibitor.
Gulati, S., Jin, H., Masuho, I., Orban, T., Cai, Y., Pardon, E., Martemyanov, K.A., Kiser, P.D., Stewart, P.L., Ford, C.P., Steyaert, J., Palczewski, K.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 1996-1996
- PubMed: 29777099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04432-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6B20 - PubMed Abstract:
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) activate heterotrimeric G proteins by mediating a GDP to GTP exchange in the Gα subunit. This leads to dissociation of the heterotrimer into Gα-GTP and Gβγ dimer. The Gα-GTP and Gβγ dimer each regulate a variety of downstream pathways to control various aspects of human physiology. Dysregulated Gβγ-signaling is a central element of various neurological and cancer-related anomalies. However, Gβγ also serves as a negative regulator of Gα that is essential for G protein inactivation, and thus has the potential for numerous side effects when targeted therapeutically. Here we report a llama-derived nanobody (Nb5) that binds tightly to the Gβγ dimer. Nb5 responds to all combinations of β-subtypes and γ-subtypes and competes with other Gβγ-regulatory proteins for a common binding site on the Gβγ dimer. Despite its inhibitory effect on Gβγ-mediated signaling, Nb5 has no effect on Gα q -mediated and Gα s -mediated signaling events in living cells.
- Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, 10900 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH, 44106, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: