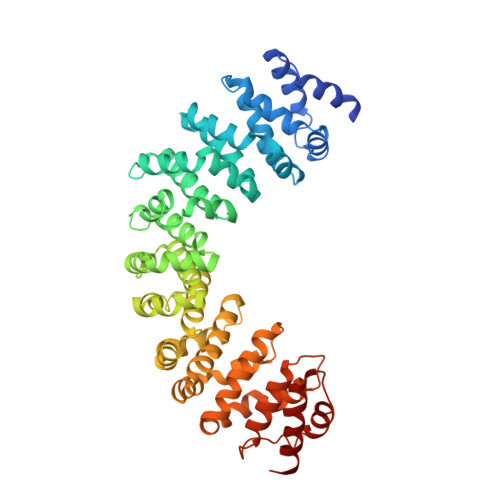
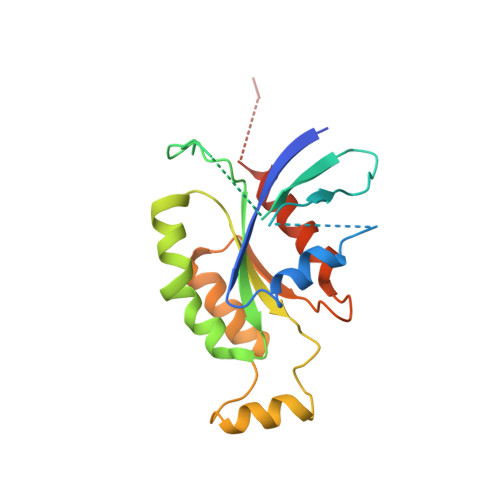
GEF mechanism revealed by the structure of SmgGDS-558 and farnesylated RhoA complex and its implication for a chaperone mechanism.
Shimizu, H., Toma-Fukai, S., Kontani, K., Katada, T., Shimizu, T.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: 9563-9568
- PubMed: 30190425
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1804740115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ZHX - PubMed Abstract:
SmgGDS has dual functions in cells and regulates small GTPases as both a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the Rho family and a molecular chaperone for small GTPases possessing a C-terminal polybasic region followed by four C-terminal residues called the CaaX motif, which is posttranslationally prenylated at its cysteine residue. Our recent structural work revealed that SmgGDS folds into tandem copies of armadillo-repeat motifs (ARMs) that are not present in other GEFs. However, the precise mechanism of GEF activity and recognition mechanism for the prenylated CaaX motif remain unknown because SmgGDS does not have a typical GEF catalytic domain and lacks a pocket to accommodate a prenyl group. Here, we aimed to determine the crystal structure of the SmgGDS/farnesylated RhoA complex. We found that SmgGDS induces a significant conformational change in the switch I and II regions that opens up the nucleotide-binding site, with the prenyl group fitting into the cryptic pocket in the N-terminal ARMs. Taken together, our findings could advance the understanding of the role of SmgGDS and enable drug design strategies for targeting SmgGDS and small GTPases.
- Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 113-0033 Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: