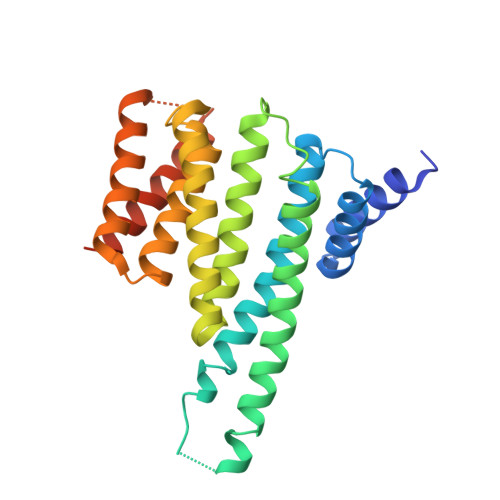
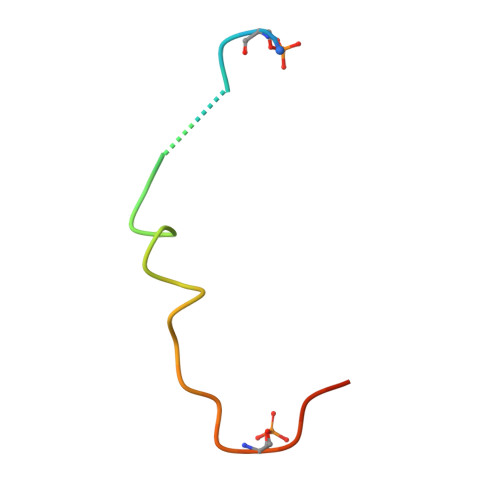
Structural determinants controlling 14-3-3 recruitment to the endocytic adaptor Numb and dissociation of the Numb/alpha-adaptin complex.
Chen, X., Liu, Z., Shan, Z., Yao, W., Gu, A., Wen, W.(2018) J Biological Chem 293: 4149-4158
- PubMed: 29382713
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000897
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YQG - PubMed Abstract:
Traffic of cargo across membranes helps establish, maintain, and reorganize distinct cellular compartments and is fundamental to many metabolic processes. The cargo-selective endocytic adaptor Numb participates in clathrin-dependent endocytosis by attaching cargoes to the clathrin adaptor α-adaptin. The phosphorylation of Numb at Ser 265 and Ser 284 recruits the regulatory protein 14-3-3, accompanied by the dissociation of Numb from α-adaptin and Numb's translocation from the cortical membrane to the cytosol. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the Numb-α-adaptin interaction and its regulation by Numb phosphorylation and 14-3-3 recruitment remain poorly understood. Here, biochemical and structural analyses of the Numb·14-3-3 complex revealed that Numb phosphorylation at both Ser 265 and Ser 284 is required for Numb's efficient interaction with 14-3-3. We also discovered that an RQFRF motif surrounding Ser 265 in Numb functions together with the canonical C-terminal DPF motif, required for Numb's interaction with α-adaptin, to form a stable complex with α-adaptin. Of note, we provide evidence that the phosphorylation-induced binding of 14-3-3 to Numb directly competes with the binding of α-adaptin to Numb. Our findings suggest a potential mechanism governing the dynamic assembly of Numb with α-adaptin or 14-3-3. This dual-site recognition of Numb by α-adaptin may have implications for other α-adaptin targets. We propose that the newly identified α-adaptin-binding site surrounding Ser 265 in Numb functions as a triggering mechanism for the dynamic dissociation of the Numb·α-adaptin complex.
- From the Department of Neurosurgery, Huashan Hospital, Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology and Department of Systems Biology for Medicine, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
Organizational Affiliation: