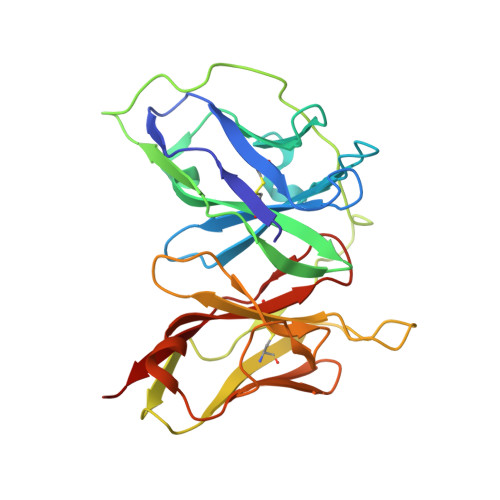
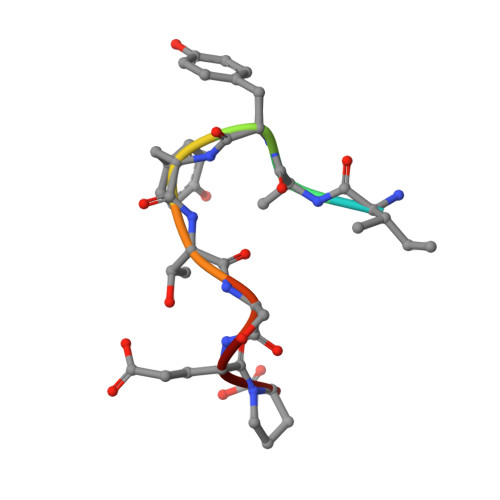
Intramolecular H-bonds govern the recognition of a flexible peptide by an antibody
Miyanabe, K., Akiba, H., Kuroda, D., Nakakido, M., Kusano-Arai, O., Iwanari, H., Hamakubo, T., Caaveiro, J.M.M., Tsumoto, K.(2018) J Biochem 164: 65-76
- PubMed: 29924367
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvy032
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YD3, 5YD4, 5YD5 - PubMed Abstract:
Molecular recognition is a fundamental event at the core of essentially every biological process. In particular, intermolecular H-bonds have been recognized as key stabilizing forces in antibody-antigen interactions resulting in exquisite specificity and high affinity. Although equally abundant, the role of intramolecular H-bonds is far less clear and not universally acknowledged. Herein, we have carried out a molecular-level study to dissect the contribution of intramolecular H-bonds in a flexible peptide for the recognition by an antibody. We show that intramolecular H-bonds may have a profound, multifaceted and favorable effect on the binding affinity by up to 2 kcal mol-1 of free energy. Collectively, our results suggest that antibodies are fine tuned to recognize transiently stabilized structures of flexible peptides in solution, for which intramolecular H-bonds play a key role.
- Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: